Reference



OpenAI's Answer
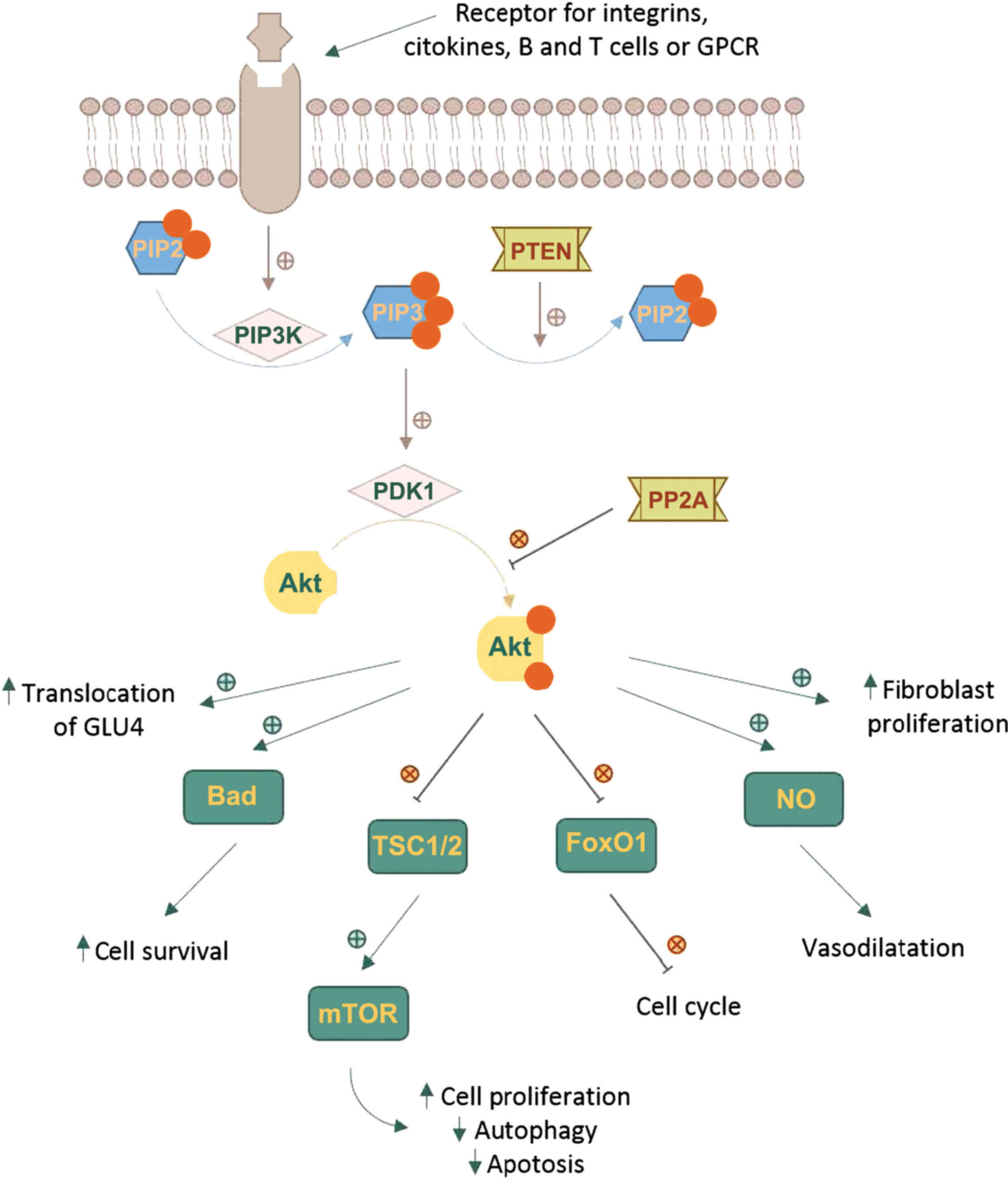
The activation of the Akt/PKB pathway plays a crucial role in cell survival by promoting cell growth, proliferation, and preventing apoptosis (programmed cell death). Akt, also known as protein kinase B, is a serine/threonine protein kinase that functions as a critical regulator of cell survival and proliferation.
When activated, Akt phosphorylates and inhibits several pro-apoptotic proteins, including Bad, Bax, and caspase-9, thereby preventing the activation of the apoptotic machinery (1). Additionally, Akt phosphorylates and activates several anti-apoptotic proteins, including NF-κB, CREB, and Bcl-xL, which promote cell survival and inhibit apoptosis (2, 3).
Akt also regulates cell metabolism by promoting glucose uptake and glycogen synthesis, which is essential for cell growth and survival (4). Furthermore, Akt activation can lead to the inhibition of autophagy, a process by which cells recycle damaged or dysfunctional organelles and proteins, thereby promoting cell survival (5).
In cancer, aberrant activation of the Akt pathway is often associated with malignancy, and Akt inhibitors are being explored as potential cancer therapeutics (6). Conversely, Akt activation can also promote cell survival in response to chemotherapy and radiation therapy, leading to resistance to these treatments (7).
In summary, the activation of the Akt/PKB pathway plays a critical role in promoting cell survival by regulating cell growth, metabolism, and apoptosis.
References:
- Datta, S. R., et al. (1997). Akt phosphorylation of BAD couples survival signals to the cell-intrinsic death machinery. Cell, 91(2), 231-241.
- Cardone, M. H., et al. (1998). Regulation of cell death protease caspase-9 by phosphorylation. Science, 282(5392), 1318-1321.
- Du, K., et al. (2003). Akt regulates cell survival and apoptosis at a postmitochondrial level. Journal of Cell Biology, 161(4), 663-672.
- Hajduch, E., et al. (2001). Insulin and insulin-like growth factor-I stimulate glycogen synthesis in human skeletal muscle cells via phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and protein kinase B. Diabetes, 50(1), 12-20.
- Wang, R. C., et al. (2012). Akt-mediated regulation of autophagy and tumorigenesis. Autophagy, 8(9), 1445-1457.
- Liu, P., et al. (2009). Targeting the PI3K/Akt pathway in cancer. Journal of Clinical Oncology, 27(33), 5521-5528.
- West, K. A., et al. (2002). Akt is a downstream target of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and mediates the survival effects of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase in human breast cancer cells. Cancer Research, 62(11), 3102-3109.
Images:
- Akt/PKB signaling pathway: http://2.bp.blogspot.com/-ZiZULi6Np94/UWwRa1P259I/AAAAAAAABNU/mKcq6yVLTgk/s1600/PKB+signaling-1.jpg
- Role of Akt in cell survival: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Nicole-Bezuidenhout-2/publication/50369780/figure/fig2/AS:669518825279488@1536637135016/A-schematic-representation-of-the-role-of-the-PI-3-kinase-PKB-Akt-pathway-in-cell.jpg
- Akt-mediated regulation of autophagy: https://www.spandidos-publications.com/article_images/ijo/53/6/IJO-53-06-2319-g00.jpg
- Akt signaling in cancer: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Jose_Fernandez34/publication/47811937/figure/download/fig7/AS:306070175141899@1449984224917/A-diagram-illustrating-the-PS-Tyro3-Akt-cell-survival-signaling-pathways.png
- Akt/PKB signaling pathway in cell metabolism: https://www.antibody-creativebiolabs.com/img/1-4-3-4-Fig1.png
Follow Up
Related
Young Mind's activation described
How do the physical education activities at AIPCS compare to traditional sports programs?
What are the primary economic activities that support Blumenort's local economy?
What activities does the Silky Terrier enjoy to stay active and avoid boredom?
Gondola2000: levi resort