Reference


OpenAI's Answer
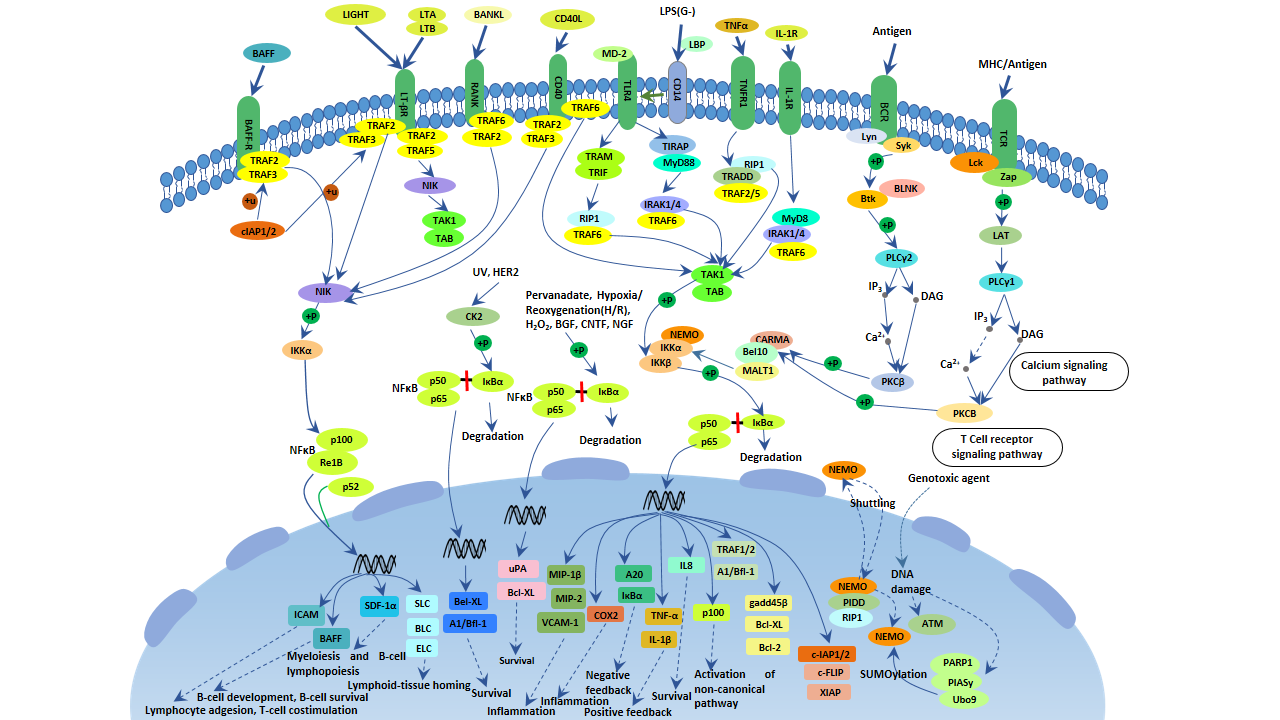
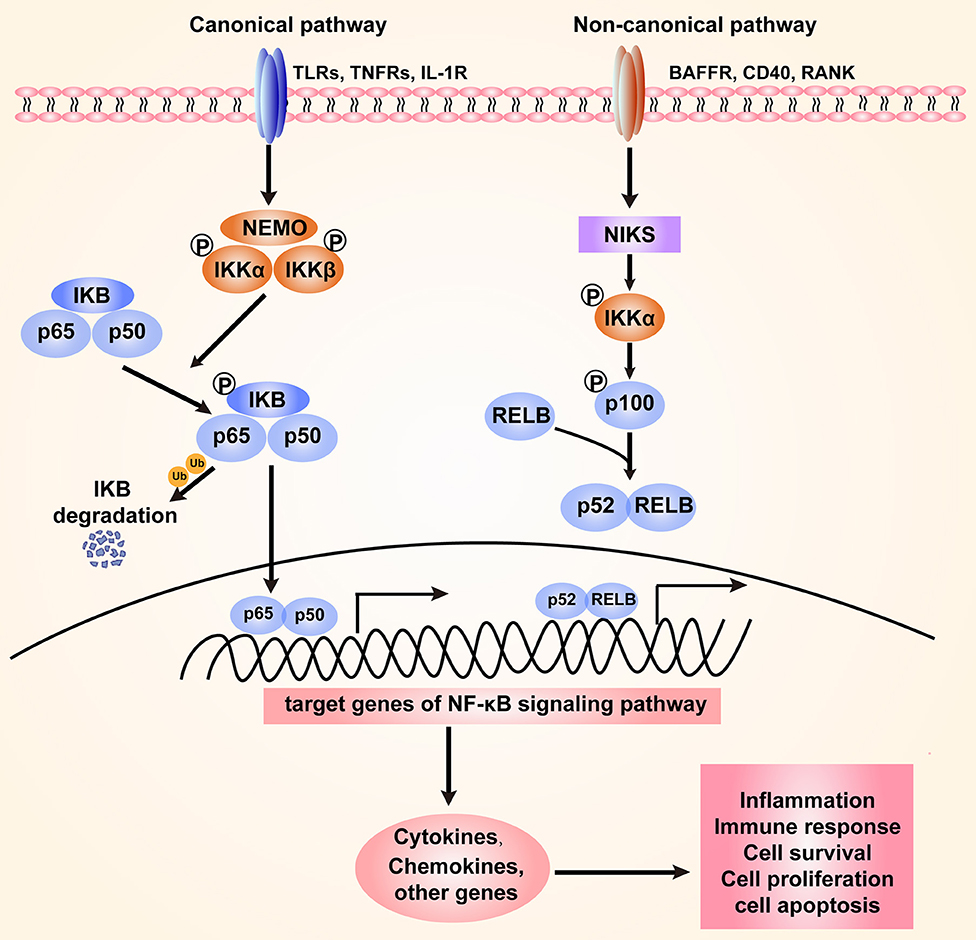
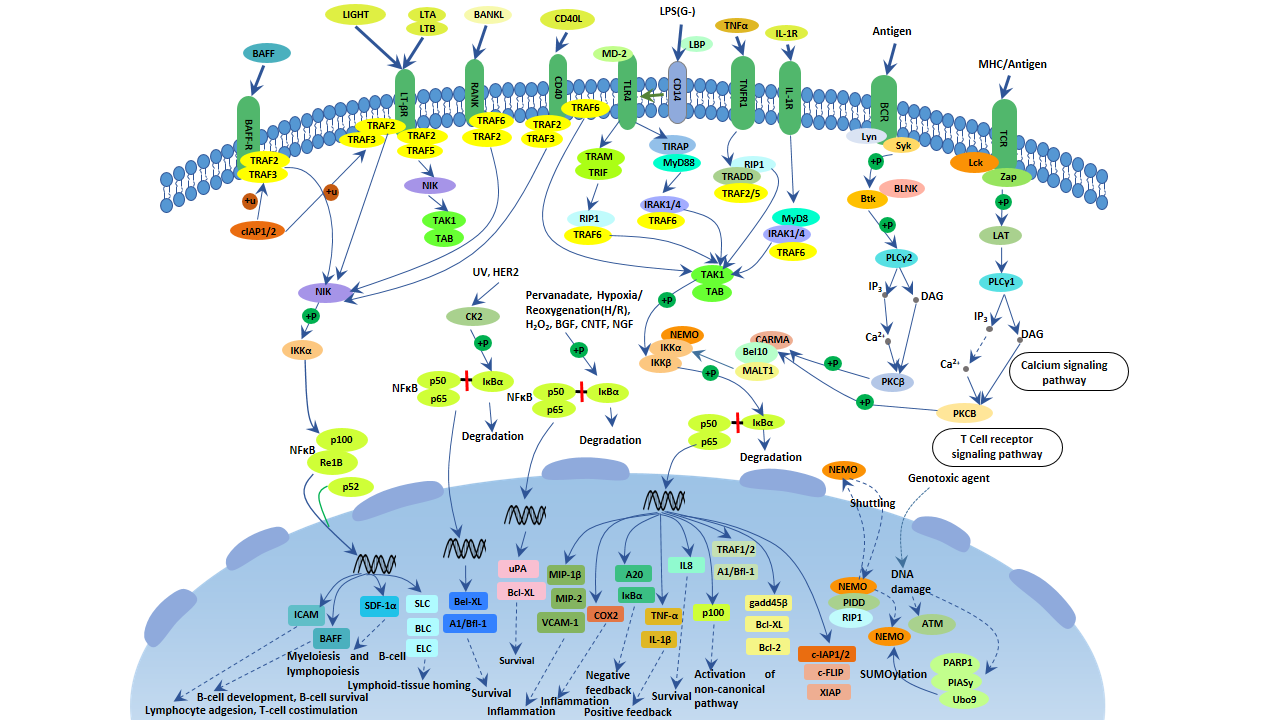
The TNF-alpha/NF-kappa B pathway is a crucial signal transduction pathway involved in inflammation, immune response, and cell survival. Here are the key components:
-
TNF-alpha (Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha): A cytokine that triggers the signaling cascade. Binding of TNF-alpha to its receptor initiates the pathway.
-
TNF Receptor (TNFR): The receptor that interacts with TNF-alpha, leading to the activation of downstream signaling molecules.
-
TRADD and RIPK1: Adaptor proteins that mediate signal transduction following TNFR activation.
-
TRAF2: A protein involved in the ubiquitination process, which is crucial for further propagating the signaling cascade.
-
IKK Complex (IκB Kinase Complex): Composed of IKKα, IKKβ, and NEMO (IKKγ), it phosphorylates IκB proteins, leading to their degradation.
-
IκB: Inhibitory proteins that sequester NF-kappa B in the cytoplasm. Upon phosphorylation and degradation, NF-kappa B is released.
-
NF-kappa B (Nuclear Factor kappa B): A transcription factor that translocates to the nucleus and activates genes involved in inflammatory and immune responses.
These components interact in a cascade where TNF-alpha binding to its receptor leads to activation and translocation of NF-kappa B from the cytoplasm to the nucleus, thus affecting gene expression.
For more detailed insights, you can read the articles on the NFκB system and a map of the TNF-alpha/NF-kappa B signal. Here is an illustrative image of the pathway:
Follow Up
Related
When was Miami University's first fraternity chapter, Alpha Delta Phi, established?
How did guest star Danny Goldring's previous Star Trek roles differ from this one?
What were some of the key sources that discussed the episode Fortunate Son?
What are the effects of tumor necrosis factor-alpha on insulin receptor substrate-4?