Reference



OpenAI's Answer
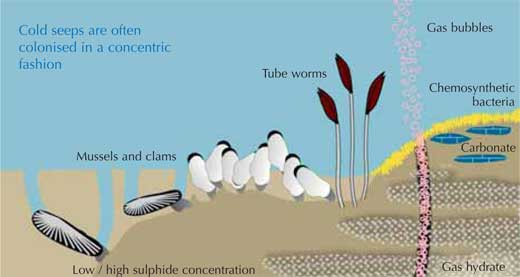
Hydrocarbon seeps have a significant impact on the ecology of serpulid worms in several ways:
-
Habitat and Bioengineering: Serpulid worms often inhabit areas around hydrocarbon seeps, where they build extensive tube systems. These tube systems alter local hydrodynamics and create complex habitats that can support diverse communities of microorganisms and other marine species (source).
-
Symbiotic Relationships: Like other tube worms in seep environments, serpulid worms can engage in symbiotic relationships with bacteria. For example, some serpulid worms have symbiotic relationships with methane-oxidizing bacteria, which provide them with nutrients by converting methane from seeps into biomass (source).
-
Ecological Roles: By forming dense colonies, serpulid worms can act as ecosystem engineers, providing structural complexity to the seabed. This can enhance local biodiversity by offering niches and substrates for other organisms to inhabit (source).
-
Adaptation to Chemosynthetic Ecosystems: The presence of hydrocarbons can lead to unique adaptations in serpulid worms. These adaptations include mechanisms to tolerate the often harsh and variable chemical conditions of seep environments (source).
-
Nutrient Cycling: Serpulid worms contribute to nutrient cycling in hydrocarbon seep ecosystems by processing organic material and influencing the distribution and abundance of other organisms through their feeding and building activities.

Follow Up
Related
What new green tools are available for delineating contaminants from past and present?
Puedes hacer un mapa conceptual de cadenas y red alimentaria (usa estás palabras: niveles troficos,
What impact does atmospheric deposition have on Bowman Creek's water quality?
Can you name some Ecological Reserves in California?