Reference


Reference




OpenAI's Answer
Signal transducing adaptor proteins and scaffold proteins play crucial roles in cellular signaling pathways by facilitating and organizing the complex interactions between proteins involved in signal transduction.
Signal Transducing Adaptor Proteins
-
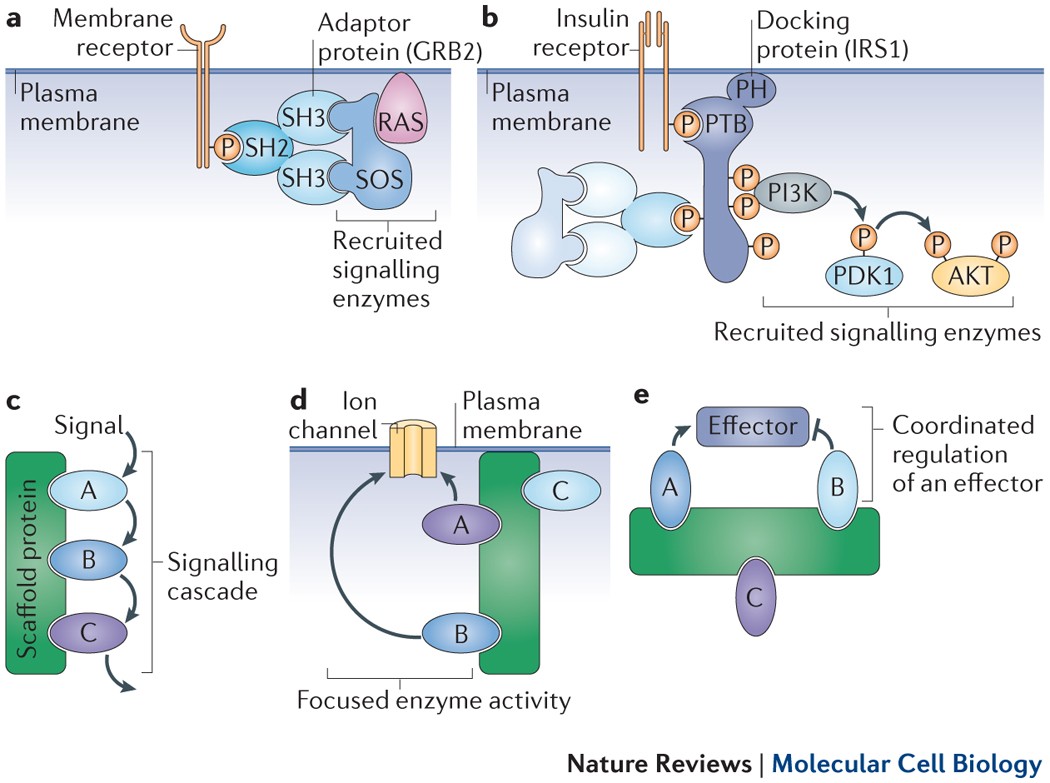
Function: Adaptor proteins serve as bridges that connect different proteins within a signaling pathway. They contain multiple binding sites that allow them to link various components of the signaling machinery, thus facilitating the assembly of signaling complexes without having catalytic activity themselves.
-
Importance:
- They are essential for the specificity and regulation of signal transduction processes.
- Adaptor proteins help integrate and propagate signals, which can lead to responses such as lymphocyte activation (source: ScienceDirect).
- These proteins play a critical role in modulating immune cell signaling, thereby having associations with human diseases (Wiley Online Library).
Scaffold Proteins
-
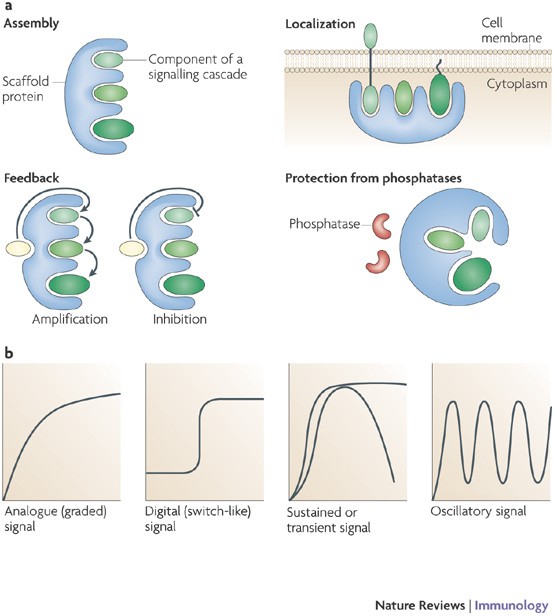
Function: Scaffold proteins act as platforms for the assembly of multiple signaling proteins into a signaling complex, thus facilitating efficient and localized signal transduction. They physically tether different signaling molecules together.
-
Importance:
- Scaffold proteins enhance the specificity and speed of the signaling processes. They help to organize efficient functional units for signaling cascades (Journal of Biological Chemistry).
- By organizing signaling complexes at specific intracellular locations, these proteins can enhance the efficacy of signaling pathways and ensure proper localization of signals (PubMed).
Overall, both adaptor and scaffold proteins are crucial for ensuring effective communication within cells, allowing cells to respond appropriately to changes in their environment. These proteins enable precise control over cellular functions and can be involved in diverse physiological and pathological processes.
Here's an illustrative image showing the scaffold protein function:
