Reference



OpenAI's Answer
Detecting abnormal PrPSc protein in brain tissue can be achieved through various methods, each offering different levels of sensitivity and specific uses. Here are the key methods identified from recent research and sources:
-
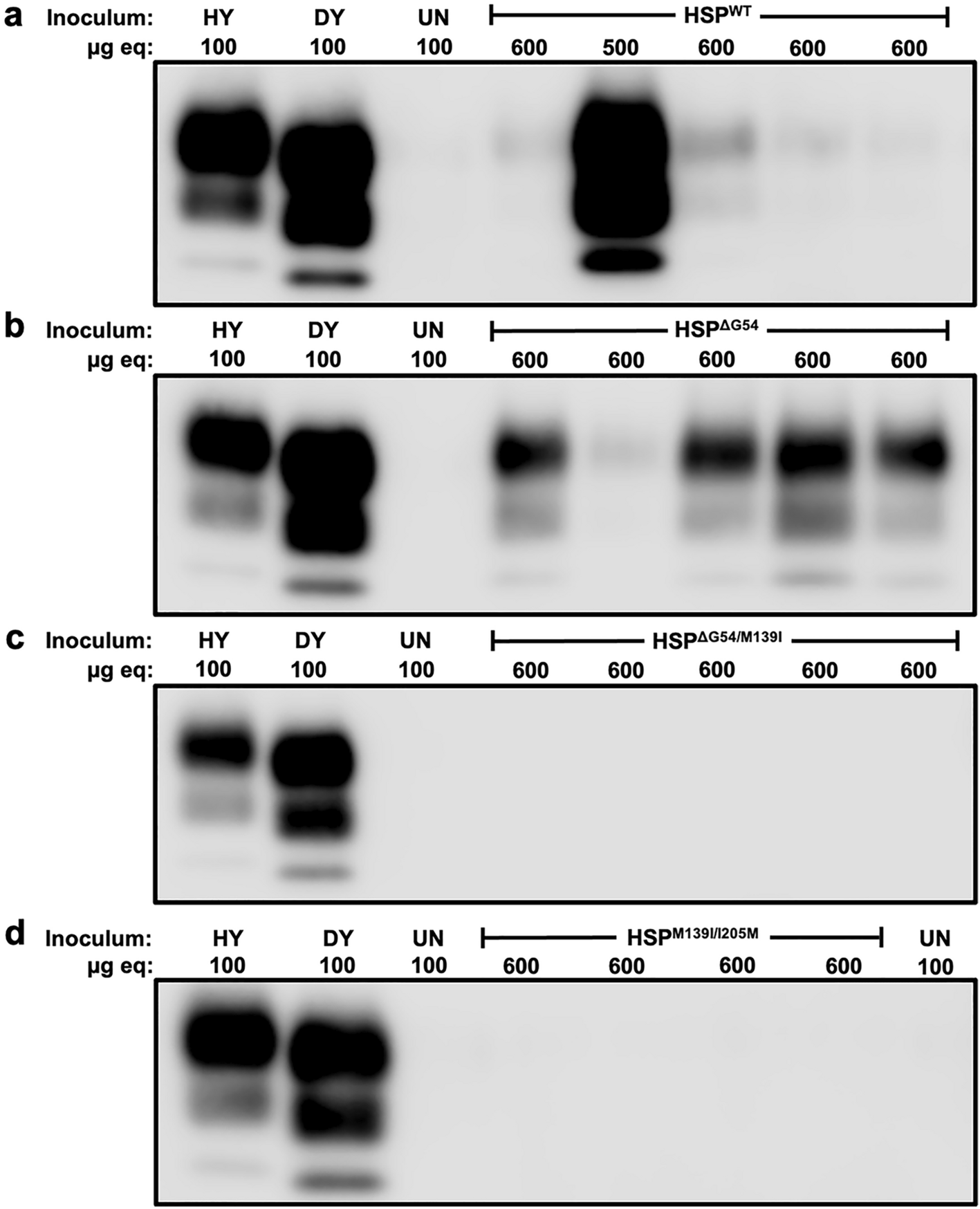
Western Blotting:
- Description: A common method where brain tissue is treated with proteinase K to digest normal prion protein (PrPC). The remaining PrPSc is detected using specific antibodies.
- Reference: ScienceDirect

-
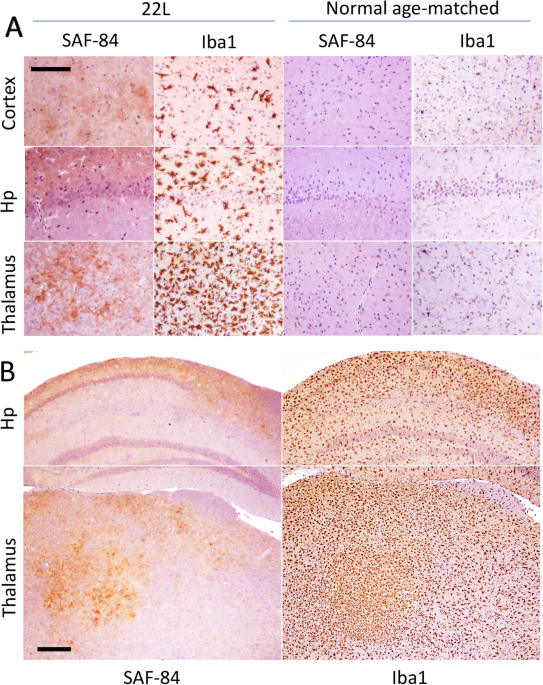
Immunohistochemistry (IHC):
- Description: This technique involves staining brain tissue sections with PrPSc-specific antibodies, allowing visualization under a microscope. It is commonly used to pinpoint the distribution of PrPSc in tissues.
- Reference: SAGE Journals
-
Real-Time Quaking-Induced Conversion (RT-QuIC):
- Description: RT-QuIC is a highly specific and sensitive method that amplifies tiny amounts of PrPSc to detectable levels. It is used for both research and clinical diagnostics.
- Reference: Case Western Reserve University

-
Conformation-Dependent Immunoassay (CDI):
- Description: This assay exploits the conformational differences between PrPSc and PrPC to detect the abnormal prion proteins using specific antibodies.
- Reference: UCSF News

-
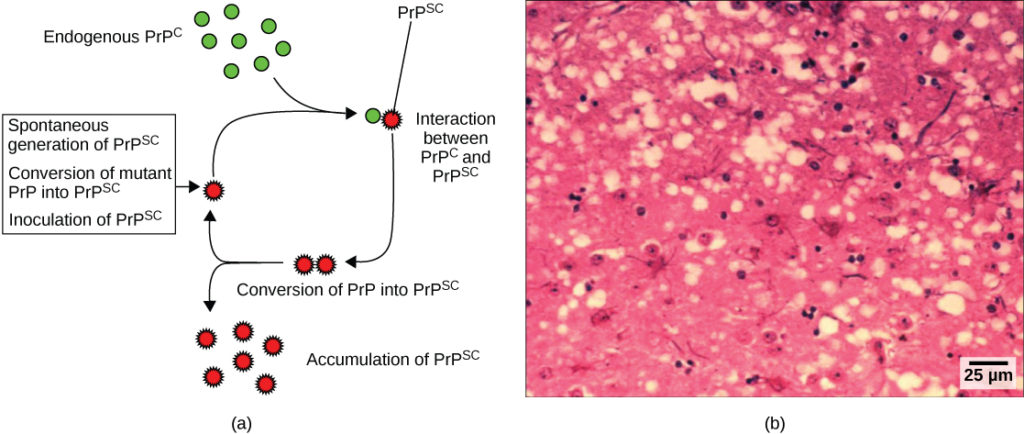
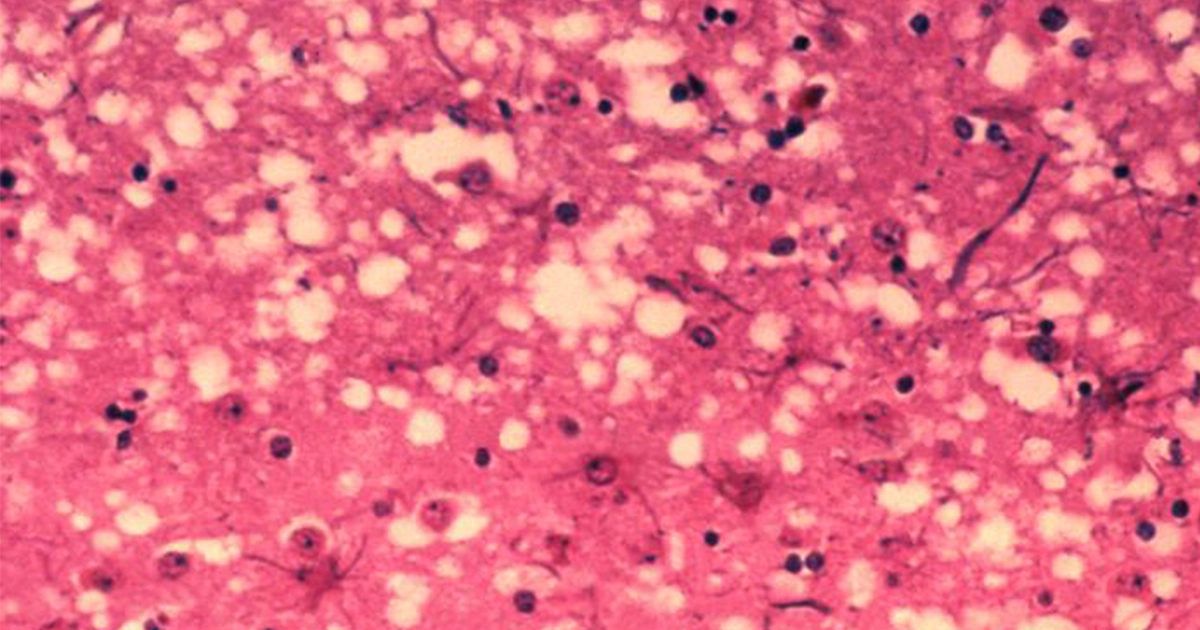
Histopathological Examination:
- Description: Traditional histopathology involves staining and examining brain tissue sections for spongiform changes and protein aggregates characteristic of prion diseases, although this method does not directly detect PrPSc.
- Reference: Johns Hopkins Medicine
-
Flow Cytometry:
- Description: A novel method using flow cytometry to detect PrPSc in neurons and glial cells, enhancing detection capabilities in specific cell types within brain tissue.
- Reference: NIH
These methods are crucial for researching prion diseases and developing effective diagnostic tools. They cover a range of techniques from direct visualization to highly sensitive amplification assays, providing comprehensive tools for the detection of PrPSc in brain tissues.
Follow Up
Related
What are the main T cell abnormalities in common variable immunodeficiency?
What are the immunological abnormalities observed in ataxia-telangiectasia patients?
What type of papers are given priority by the Journal of Abnormal Psychology?
What are the major areas of focus for the Journal of Abnormal Psychology?