Reference


OpenAI's Answer
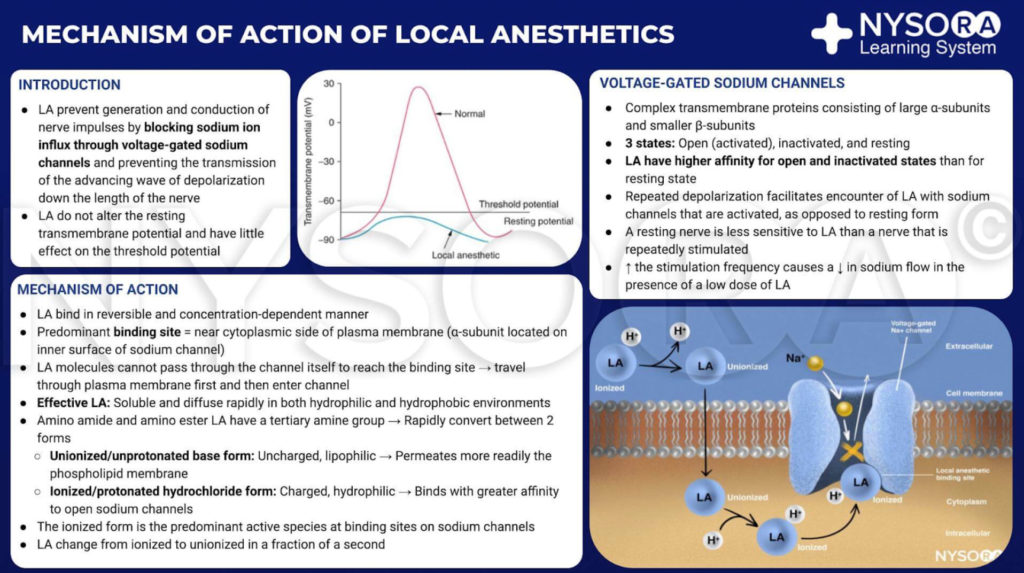
Nisoxetine exhibits potential local anesthetic effects primarily through its action on voltage-gated sodium channels (VGSCs). Local anesthetics work by inhibiting these sodium channels, which are essential for the conduction of nerve impulses. This inhibition results in a decrease in nerve excitability and ultimately blocks the transmission of pain signals.
Nisoxetine, typically known as a selective norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor, also blocks sodium currents, which is associated with its spinal anesthesia effects in research studies. By blocking VGSCs, nisoxetine disrupts the action potentials that are responsible for transmitting sensory information, thereby producing local anesthetic effects.
Here are some relevant sources for further reading:
- Nisoxetine blocks sodium currents and elicits spinal anesthesia in rats
- Nisoxetine produces local but not systemic analgesia against pain