Reference

OpenAI's Answer
Prions play a crucial role in the development of transmissible spongiform encephalopathies (TSEs), a group of fatal neurodegenerative diseases. Here's an overview of the role they play:
-
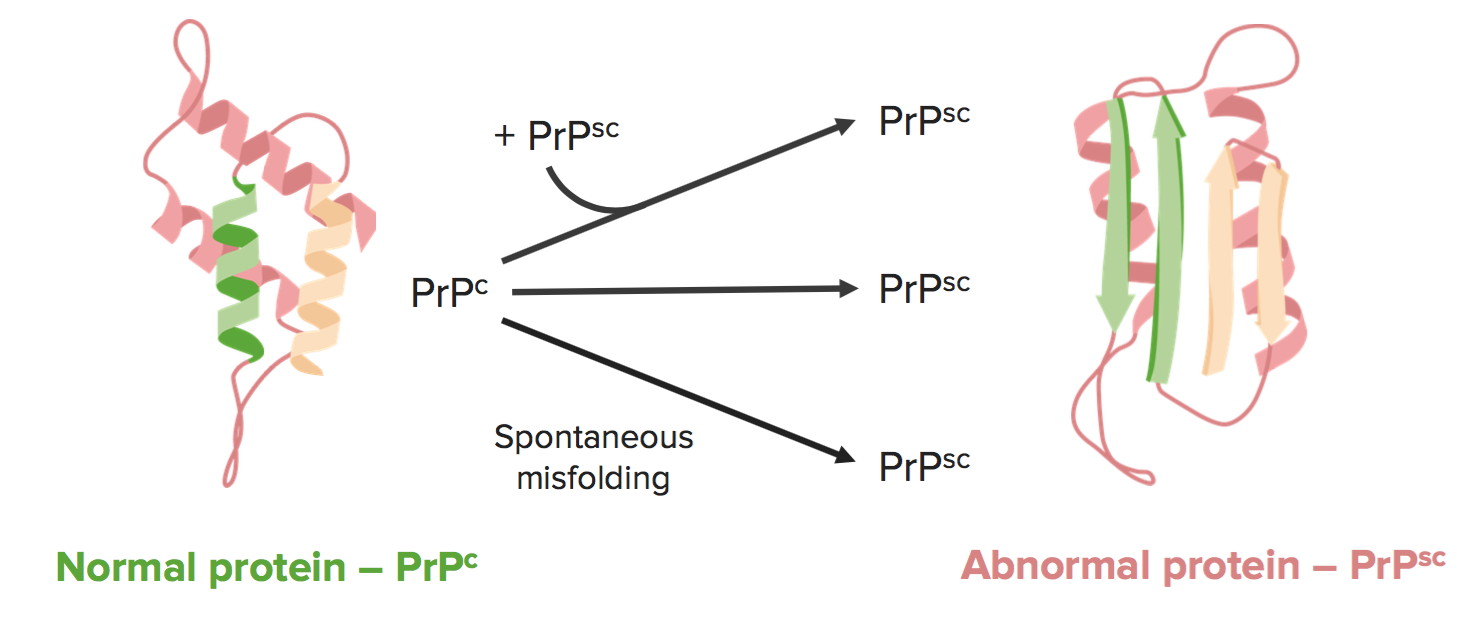
Misfolding of Prion Proteins: Prions are abnormally folded proteins that can induce other normally folded proteins (PrP^C) to also misfold into the disease-causing form (PrP^Sc). This misfolding is central to the pathology of TSEs (CDC).
-
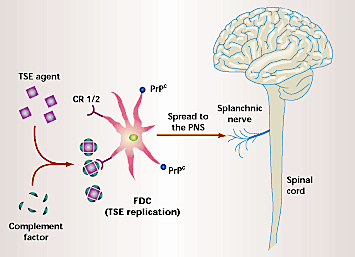
Brain Damage and Symptoms: The accumulation of these misfolded prion proteins in neural tissue leads to brain damage, which manifests as spongiform changes where the brain tissue develops holes and takes on a spongy texture. This results in the severe neurological symptoms characteristic of TSEs (Physio-Pedia).
-
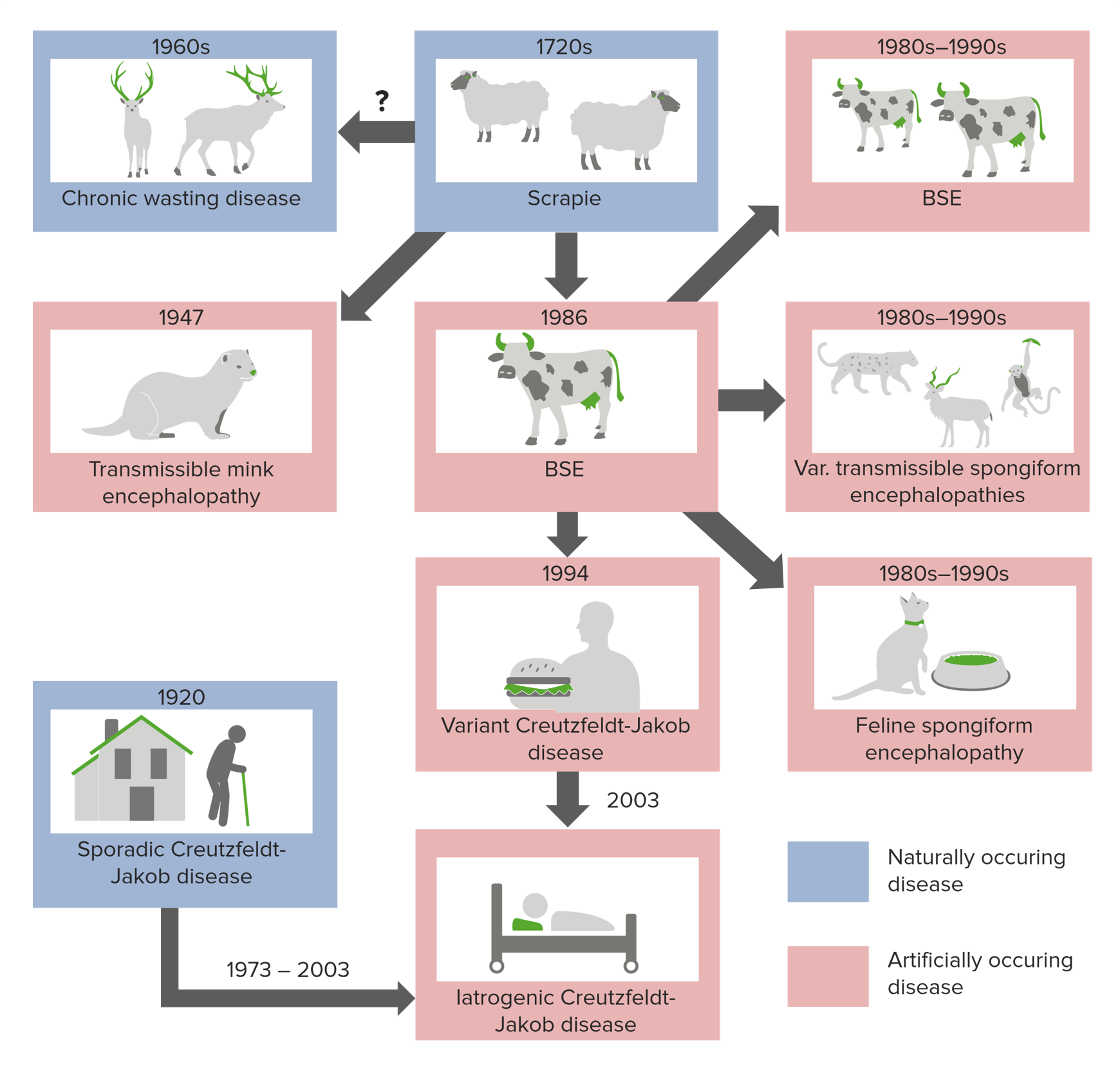
Propagation and Infection: Prions are uniquely infectious; they can be transmitted between individuals and across species through ingestion of infected tissue, blood transfusions, and other routes. Once introduced into a new host, prions continue to propagate by converting normal prion proteins into the pathogenic form (ScienceDirect).
-
Diverse Diseases: TSEs encompass multiple diseases, including Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD), mad cow disease (BSE), scrapie in sheep, and chronic wasting disease in deer. Despite their different names and affected species, all these diseases are caused by similar prion-related mechanisms (Health.state.mn.us).
Visual Representation
 This image depicts the propagation of misfolded prion proteins, further explaining how prions convert normal proteins into the abnormal form.
This image depicts the propagation of misfolded prion proteins, further explaining how prions convert normal proteins into the abnormal form.
 Spongiform changes are visible in the brain tissue of a patient with Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease, explaining the pathology behind TSEs.
Spongiform changes are visible in the brain tissue of a patient with Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease, explaining the pathology behind TSEs.
For a deeper understanding, refer to these sources:
Follow Up
Related
How did economic changes influence the population and development of North and South Carolina?
Can you name some unmanned surface vehicles developed by CASIC?
Which organizations provided the final approval for the New Balance development?
How does the free software movement influence software development?
What major development project was associated with Boston Landing station?