Reference


OpenAI's Answer
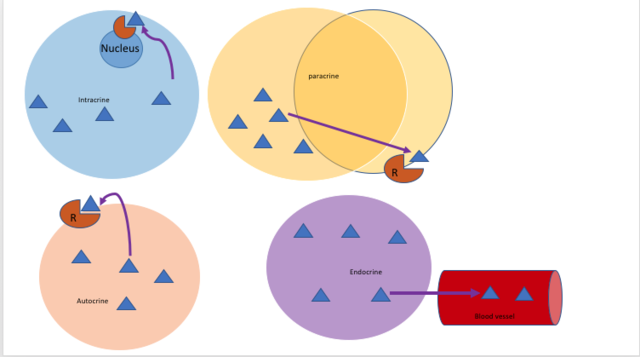
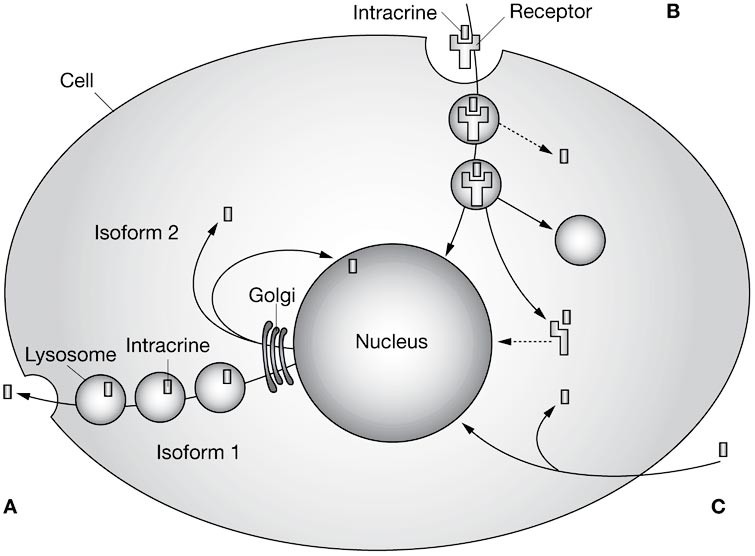
Peptides that function through intracrine mechanisms include several hormones that can act inside the cells they are synthesized in, or in target cells after being internalized. Here are some examples:
-
Angiogenin: This peptide hormone is known for its role in promoting blood vessel formation and has demonstrated intracrine activity. It functions within cells, impacting processes such as cell growth and survival source.
-
Parathyroid Hormone-related Protein (PTHrP): This protein has intracrine functionalities, contributing to various physiological processes within the cell, including regulation of gene expression source.
-
VEGF-A (Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor A): It plays a significant role in intracrine signaling, especially concerning cell growth, differentiation, and survival. This peptide acts within the cells influencing normal cellular homeostasis and pathology source.
These peptides exemplify how intracrine signaling can impact cellular processes from within, contrasting with more traditional extracellular signaling pathways.