Reference
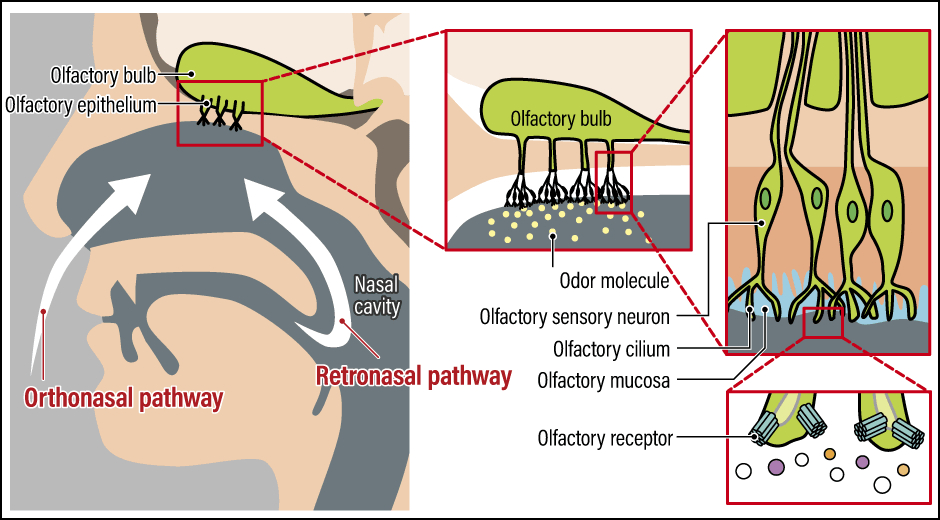



Moonshot's Answer
The evolutionary advantages that humans might have developed through superior retronasal smell include:
-
Enhanced Food Identification and Nutritional Assessment: Superior retronasal smell allows humans to better identify and assess the nutritional value of food, which is crucial for survival and health. This ability to discern flavors and aromas can guide food choices and improve dietary intake, as suggested by the article "Olfaction enabling us to savor tasty flavors could hold the key to ..." Healthist.
-
Social and Mate Selection: Humans can use their sense of smell to select mates, as body odors can signal genetic compatibility and health status. This is supported by the article "Prelude: Darwin, Smell, and Evolution | Art Scents - Oxford Academic" Oxford Academic, which discusses how humans can enhance their natural odor to make themselves more attractive.
-
Detection of Spoiled Food: The ability to detect spoiled or contaminated food through retronasal smell helps humans avoid foodborne illnesses, as indicated in the article "How losing a bone in our noses gave us the ability to enjoy flavour" New Scientist.
-
Improved Cooking and Food Preparation: The unique configuration of the human pharynx and the ability to enhance retronasal olfaction may have played a role in the development of cooking skills, as suggested by "How the unique configuration of the human head may enhance ..." Frontiers in Neuroscience.
-
Enhanced Flavor Perception: Retronasal smell is a key component of flavor perception, which is essential for enjoying food and possibly for social bonding over meals. This is supported by "Smelling odours and tasting flavours: Distinguishing orthonasal ..." Oxford Academic.
-
Navigation and Environmental Awareness: Humans can track odors to navigate and assess their environment, which is an advantage in both hunting and avoiding predators, as mentioned in "Smell with inspiration: The evolutionary significance of olfaction" Wiley Online Library.
These advantages highlight the importance of retronasal smell in human evolution, contributing to survival, social interaction, and cultural development.