Reference



OpenAI's Answer
Parathyroid hormone-related protein (PTHrP) has diverse roles, particularly when it functions as an intracrine factor. Here are some key functional consequences of PTHrP acting intracrinally:
-
Nuclear Access and Function Regulation: PTHrP can enter the nucleus and nucleolus, affecting gene expression and altering cellular functions directly at the genetic level. This capability allows PTHrP to regulate different cellular processes from within the cell. [source]
-
Role in Tumorigenesis: Different regions of PTHrP can have contrasting effects on cancer growth. For instance, the nuclear localization sequence (NLS) of PTHrP may act as a tumor suppressor, while other sequences may promote tumor growth by functioning as oncogenic factors. [source]
-
Cellular Proliferation and Survival: Intracrine action of PTHrP may promote cell proliferation and survival. It acts as a mitogenic factor that helps in cell growth and can reduce apoptosis, supporting cell longevity and tissue maintenance. [source]
-
Physiological Regulation: PTHrP impacts physiological processes, such as the regulation of chondrocyte differentiation in bone, which is crucial in bone development and remodeling. It is involved in the balance between bone formation and resorption. [source]
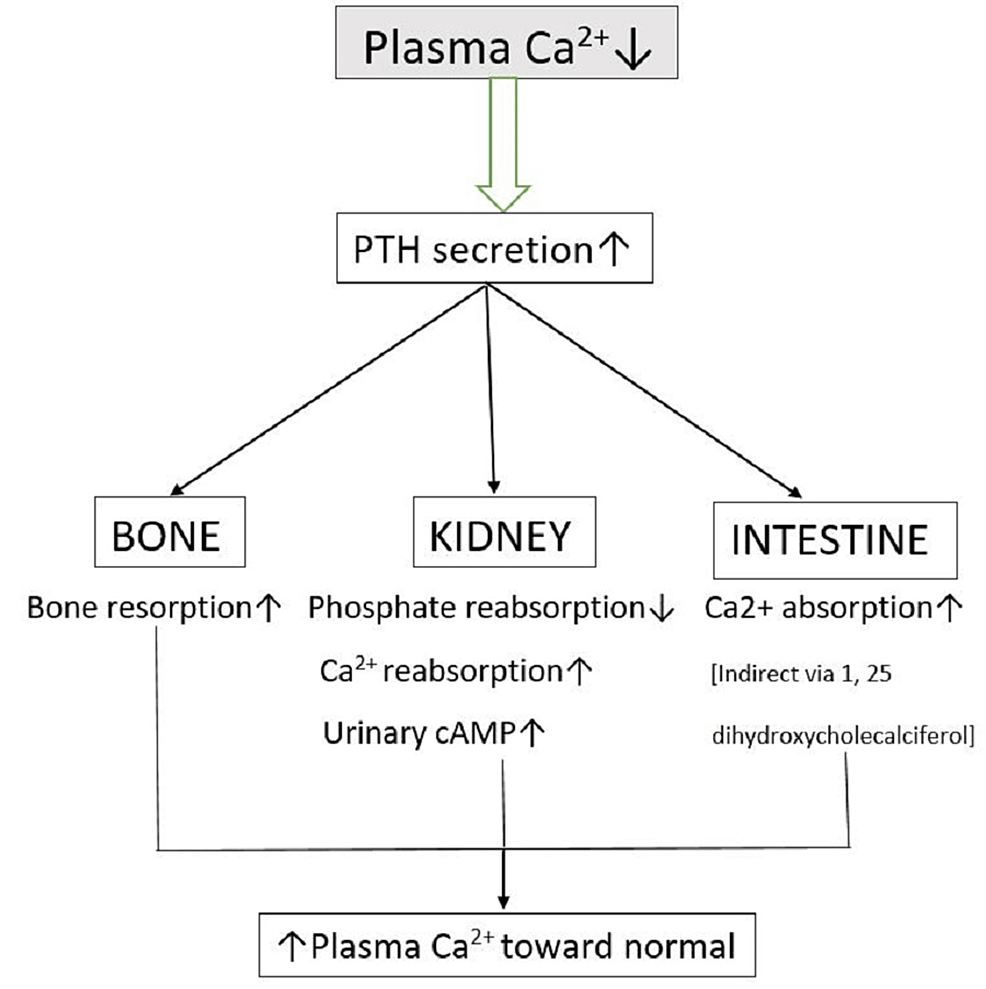
These functions showcase the multifaceted roles of PTHrP as an intracrine factor, impacting both physiological and pathological processes. Below is an image that visually represents its signaling pathways:
Follow Up
Related
What are the main counterarguments against the abiogenic origin of petroleum?
websites to read books by Billiejo Priestley
What are the major contributions of Louise Baur in the field of paediatric obesity?
What challenges does Salt Lake City face regarding homelessness and its related policies?
What was the purpose of Nassau County Jail built in 1900?
How many world records were broken on the first day of the Championships?