Reference



Moonshot's Answer
Lateral inhibition and gain compression are two important concepts in the context of olfaction, or the sense of smell.
-
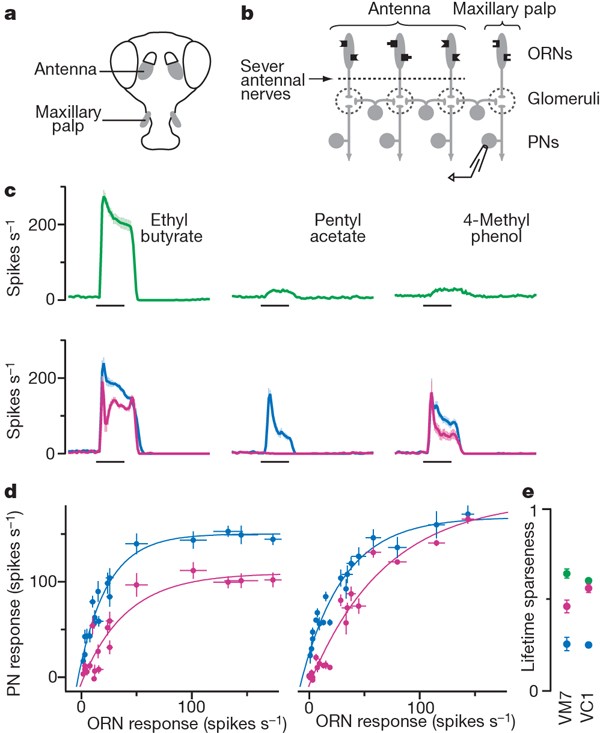
Lateral Inhibition: This is a neural mechanism that enhances the contrast between different stimuli by inhibiting the activity of neurons that respond to less intense or less relevant inputs. In the context of smell, lateral inhibition helps in odor discrimination by decreasing the firing rate of neurons in response to background odors, thus allowing the brain to focus on the more intense or behaviorally relevant odors [1]. It is also involved in normalizing the responses of projection neurons (PNs) in the olfactory system, making them less sensitive to odor concentration but more sensitive to the quality of the odor [3]. This mechanism is thought to help distinguish between similar odors and enhance the transmission of odor information to downstream neurons [5].
-
Gain Compression: This refers to the process by which the output of a sensory system is adjusted to match the input intensity. In the context of smell, gain compression is a way to normalize the input from different odor concentrations, ensuring that the neural response is not overwhelmed by strong odors and is still sensitive to weak odors. This is achieved through a combination of lateral inhibition and other neural processes that adjust the sensitivity of the olfactory system based on the intensity of the odor stimulus [4]. The end result is that the olfactory system can represent a wide range of odor concentrations in a more uniform way, which is important for odor perception and discrimination [6].
In summary, lateral inhibition and gain compression are key neural mechanisms that help the olfactory system to process a wide range of odor stimuli effectively, enhancing our ability to discriminate and perceive different smells. These mechanisms contribute to the dynamic range and sensitivity of our sense of smell.
Follow Up
Related
introduction of four stroke petrol engine
# Comprehensive Multimedia Memory Sharing Platform ## Project Vision Develop a full-featured web
How were the approved schools different from borstals in the UK?
How does nisoxetine compare to lidocaine regarding potency and duration of cutaneous anesthesia?