Reference



OpenAI's Answer
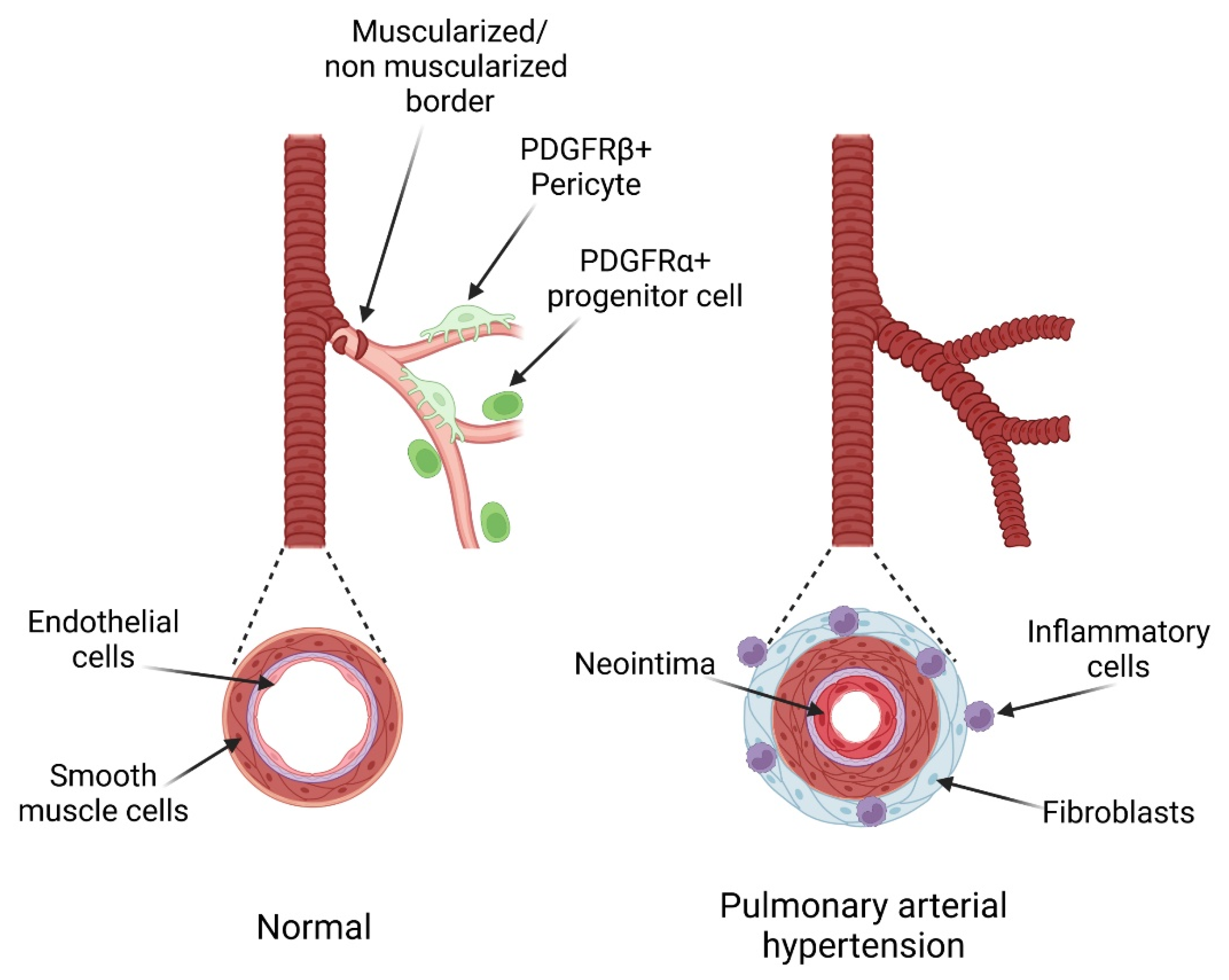
Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) plays a significant role in blood vessel formation, a process known as angiogenesis. PDGF is a type of growth factor that regulates cell growth and division, especially in cells that form part of the structure of blood vessels. Here are some key points regarding its contribution:
-
Stimulation of Cell Proliferation: PDGF promotes the proliferation of mesenchymal cells such as fibroblasts, osteoblasts, and vascular smooth muscle cells. These are essential components in the building and remodeling of blood vessel walls Wikipedia.
-
Role in Embryogenesis: During embryonic development, PDGFs are vital for the formation of blood vessels, guiding mesenchymal cell migration, proliferation, and chemotaxis to form the new vascular structures necessary for proper tissue vascularization NCBI.
-
Interaction with Receptors: PDGF interacts with specific receptors (PDGFR), playing crucial roles in signaling pathways that regulate these cellular processes. These interactions are essential for proper blood vessel formation and also in the maintenance and repair of the vascular system NCBI.
Here is an illustrative image that depicts the role of PDGF in blood vessel formation:

These integrated activities of PDGF and its receptors make it an important component in both developmental and adult angiogenic processes.