Reference


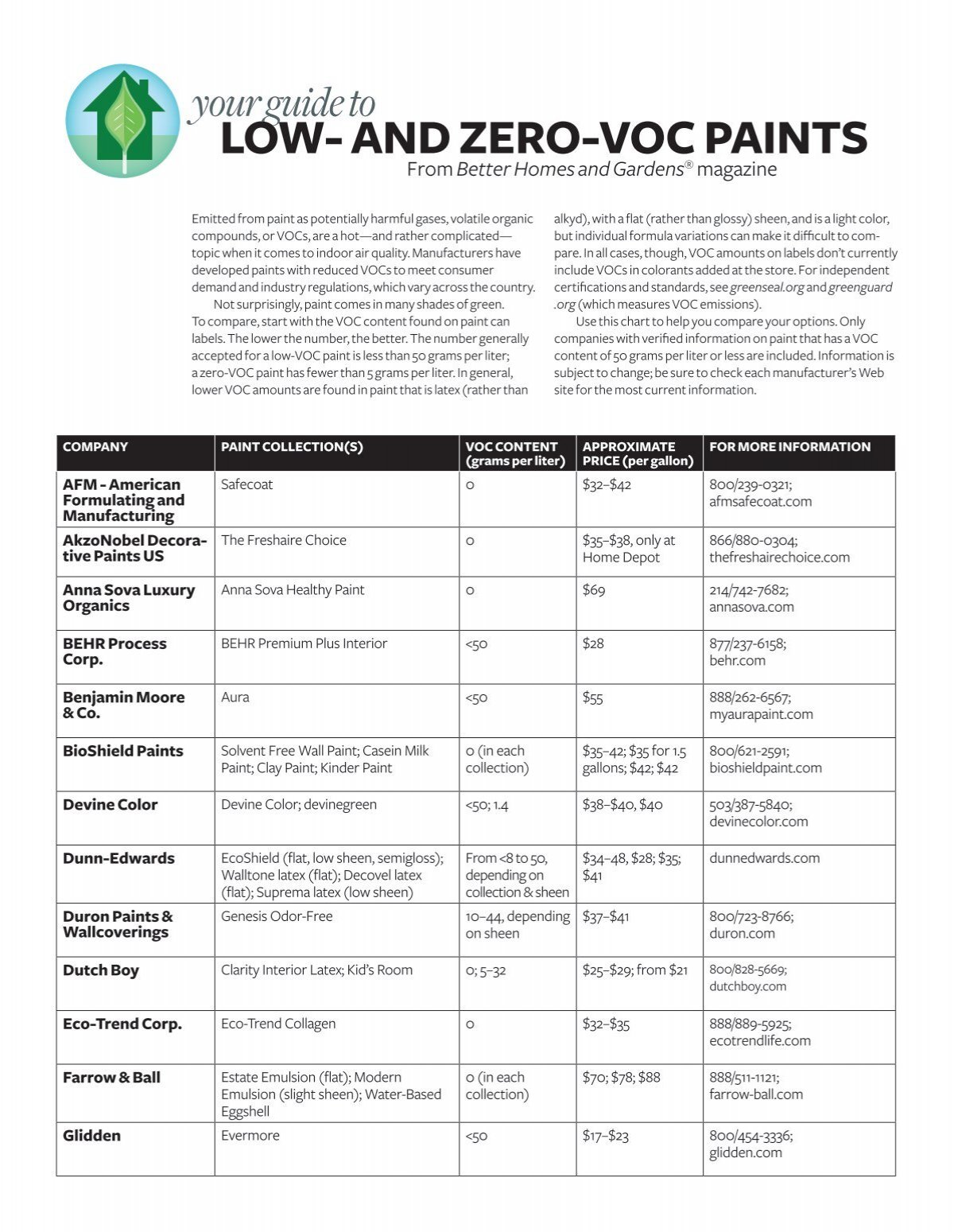

OpenAI's Answer
Advancements in low-VOC and zero-VOC paints have been driven by a growing demand for eco-friendly products that minimize environmental and health impacts. These paints are formulated with minimal volatile organic compounds (VOCs), which are chemicals that can release toxic fumes into the air and contribute to air pollution. Over the years, significant technological and chemical innovations have enhanced the performance, cost-effectiveness, and availability of low-VOC and zero-VOC paints. Here's a breakdown of key advancements in this field:
1. Improved Raw Materials and Resin Technology
One of the most substantial advancements in low- and zero-VOC paints has been the evolution of resin technology. Early formulations from the 1990s were relatively limited and inefficient, but today’s products use more advanced resins, offering better durability and performance. This shift has enabled the creation of paints that not only contain low or no VOCs but also provide long-lasting finishes and enhanced resistance to wear and tear .
Example: The introduction of new cross-linking monomers has improved the performance of polymer-based paints. These monomers help create stronger and more resilient coatings without relying on high-VOC chemicals .
2. Innovations in Coalescents
Coalescents are essential in helping water-based paints form a solid film as they dry. For zero-VOC formulations, new types of coalescents have been developed that emit negligible levels of VOCs during application. For example, ultra-low VOC and zero-emission coalescents have been formulated to work effectively with water-based paints, facilitating the transition from solvent-based to more environmentally friendly options without compromising the quality or application properties of the paint .
3. Advancements in Pigments and Colorants
Another major area of innovation lies in the development of new pigments and colorants that work with low- and zero-VOC paints. In the past, many pigments contained organic solvents that emitted VOCs. Today, environmentally friendly pigments are being used that do not release harmful chemicals, ensuring that both color and environmental impact are optimized .
4. Enhanced Durability and Performance
Although early low- and zero-VOC paints sometimes faced criticisms for lackluster durability, modern formulations have significantly improved. New additives and curing agents have been developed that allow these paints to maintain high performance, including resistance to fading, dirt, and abrasion. These advances have led to more widespread acceptance of zero-VOC paints in both residential and commercial applications, where durability is key .
5. Increased Market Acceptance
The market for zero-VOC and low-VOC paints has expanded considerably. Major paint brands like Benjamin Moore, Sherwin-Williams, and Dunn-Edwards now offer a variety of these paints in different finishes and colors, making them accessible to a broader consumer base. This widespread availability has helped shift public opinion, particularly among those concerned about indoor air quality, environmental impact, and health .
Example: Benjamin Moore’s Eco Spec and Aura lines, for instance, offer products that are near-zero VOC while maintaining excellent coverage and a wide range of colors .
6. Regulatory Support and Standards
Government regulations and environmental standards have played a critical role in promoting the development of low-VOC and zero-VOC paints. The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has set strict limits on VOC levels in paints, which has driven manufacturers to innovate and create formulations that meet or exceed these standards. Additionally, certifications like GREENGUARD and the LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) rating system encourage the use of low-VOC and zero-VOC products in green building projects .
7. Technological Integration and Smart Coatings
The latest frontier for paint technology includes the integration of smart coatings that can further enhance environmental performance. Some new formulations have been designed with antimicrobial properties, UV protection, and even self-cleaning capabilities. These technologies can reduce the overall maintenance required for surfaces, further extending the life of coatings and minimizing the need for frequent repainting .
8. Sustainability and Corporate Responsibility
As more consumers demand environmentally responsible products, paint manufacturers are investing in sustainable practices. This includes sourcing raw materials that are renewable or recycled, using energy-efficient manufacturing processes, and developing packaging that is either recyclable or made from post-consumer materials .
9. Emerging Alternatives: Powder Coatings
Powder coatings, which emit negligible to zero VOCs, are becoming an increasingly popular alternative to traditional liquid-based paints. These coatings are especially useful in industrial applications but are also finding their place in residential areas for certain applications, such as appliances, furniture, and architectural elements. However, the challenge with powder coatings remains in the control of color consistency and the complex application process .
10. Health and Safety Considerations
Zero-VOC paints, in particular, are being developed with a focus on health and safety. VOCs in traditional paints can cause headaches, dizziness, and respiratory issues. In contrast, low-VOC and zero-VOC paints minimize these risks, offering a safer environment for both consumers and professional painters. Many of these paints are also free from other toxic chemicals like formaldehyde and phthalates .
Conclusion
The advancements in low-VOC and zero-VOC paints reflect significant progress in the paint industry’s effort to reduce environmental impact while maintaining high performance. With innovations in raw materials, coalescents, and pigments, as well as improved durability and ease of use, these eco-friendly options are now more viable than ever. Whether for residential, commercial, or industrial applications, low- and zero-VOC paints are helping to make the world a safer, healthier place to live and work.
Follow Up
Related
How many points did Deportivo Municipal (Quillabamba) accumulate to advance in their group?
How are the racial disparities in advanced placement classes at Columbia High School?
Which teams advanced to the Second stage from the Andean Zone Group B?
What recent advancements have been made in macrocyclic fluorescent ion probes?