Reference


OpenAI's Answer
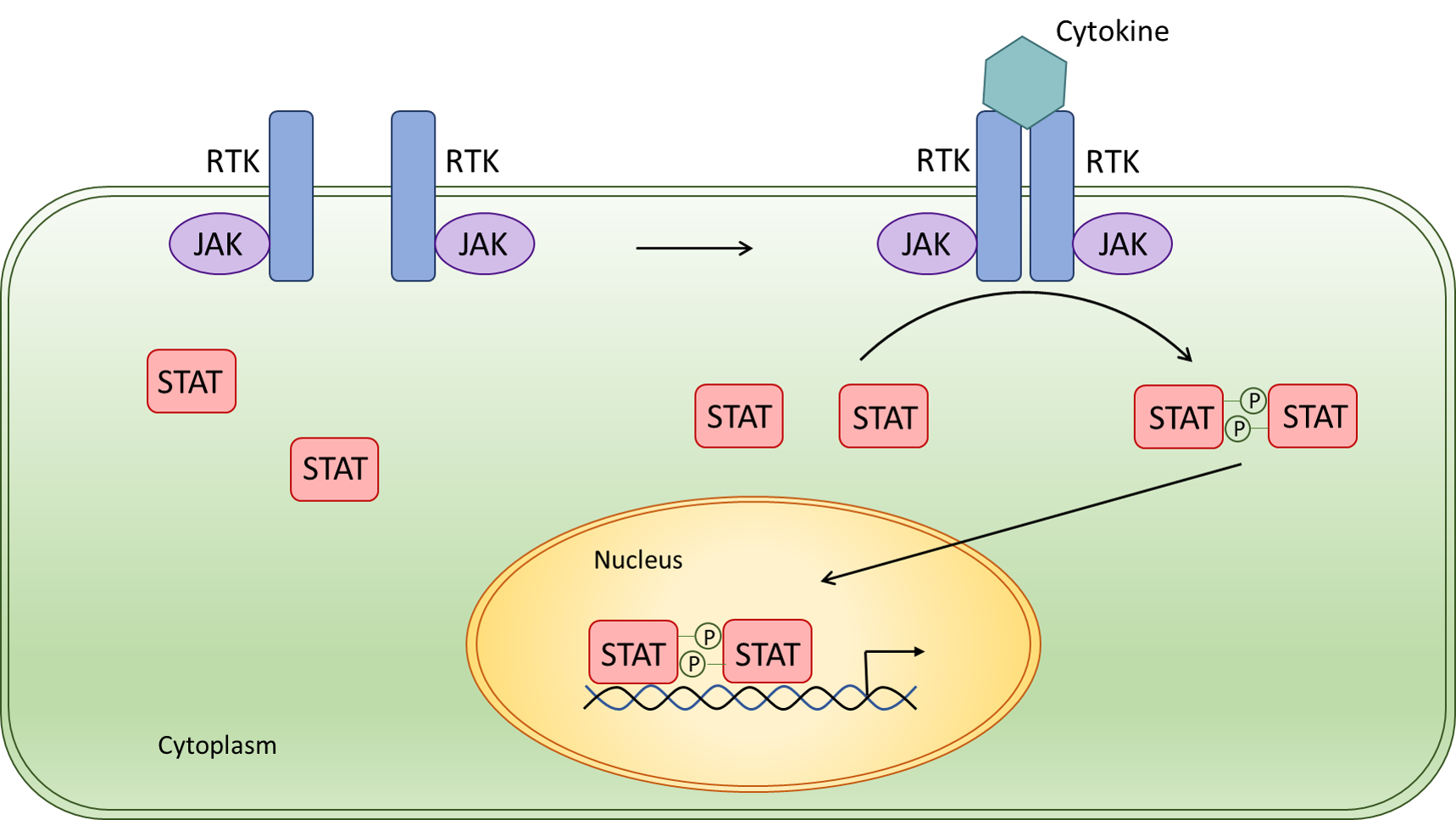
The JAK-STAT signaling pathway plays a critical role in cell growth, survival, differentiation, and immune response, and it is frequently implicated in cancer development and progression. Here's how it is related to oncogenes:
-
Overactivation and Cancer: The JAK-STAT pathway can become oncogenic when it is aberrantly activated. Overactivation of this pathway bypasses the normal cell cycle checkpoints and apoptosis, leading to uncontrolled cell proliferation, which is a hallmark of cancer source.
-
Mutation-Induced Activation: In cancer, mutations in JAK kinases can lead to their autoactivation without the normal ligand-induced signaling events. This results in continuous activation of the downstream STAT proteins, contributing to oncogenesis source.
-
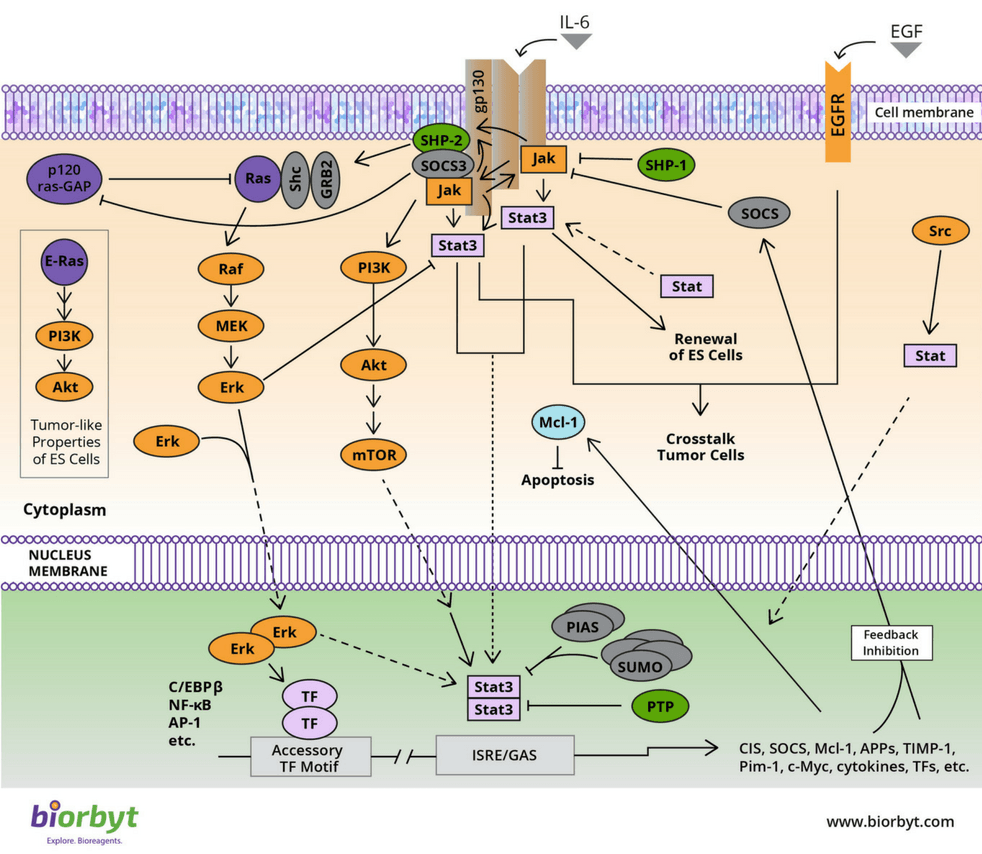
Involvement in Hematological Malignancies: Specifically, the JAK-STAT pathway is known to be heavily implicated in hematological malignancies. This pathway has a central role in cytokine signaling, which is crucial for cell proliferation, survival, and immune response, thus its dysregulation contributes to the malignancy source.
-
Inflammation and Cancer Linkage: The JAK-STAT pathway also links inflammation with cancer development, tumor progression, and therapy resistance. For example, its activation can lead to the expression of proteins that help tumors evade the immune system’s cytotoxic responses source.
For visual insights, here is a representation of the JAK-STAT signaling pathway:

The interplay between the JAK-STAT pathway and oncogenesis underscores its potential as a target for cancer therapies, aiming to inhibit aberrant signaling and thereby control cancer progression.
Follow Up
Related
What are common applications of JAK inhibitors in medical treatments?
How does 12/15-lipoxygenase contribute to PDGF-induced activation of STAT3?
What mechanisms lead to divergent effects of growth factors in stem cell differentiation?
Which signaling pathways are involved in cell signaling and signal transduction?