Reference

Moonshot's Answer
Galectins and their ligands play significant roles in inflammation, as indicated by the search results:
-
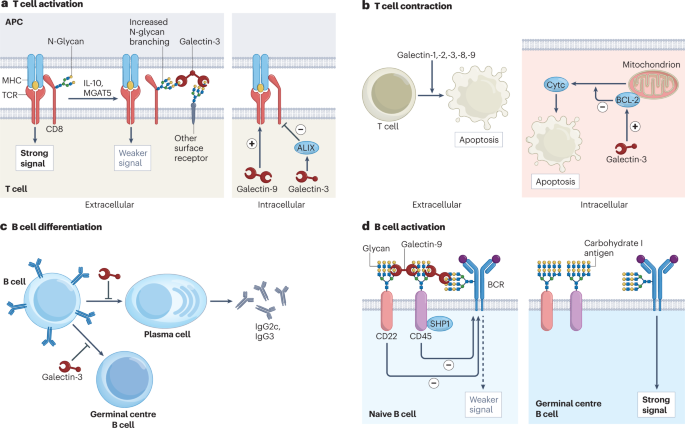
Modulation of Immune Cells: Galectins can modulate adaptive immune cells through both intracellular and extracellular mechanisms, affecting antigen-presenting cells and T-cell selection in the thymus 1 2.
-
Inflammatory Resolution: Galectins act as mediators of inflammatory resolution phases due to their pro-apoptotic activities on activated immune cells 3.
-
Regulation of Inflammation: Several galectins are key regulators of inflammation, with some involved in the regulation of metabolic pathways 4.
-
Fibrosis and Inflammation: Galectin-3 is a key player in fibrosis and inflammation in various organs, including the heart, liver, kidneys, and lungs 5.
-
Neuroinflammation: Galectin-1 and Galectin-3 play important roles in neuroinflammatory and neurodegenerative disorders such as multiple sclerosis 6.
-
Neutrophil Migration and Removal: Galectin-3 increases neutrophil migration to inflamed tissues and participates in their removal, which is critical for terminating inflammation 7.
-
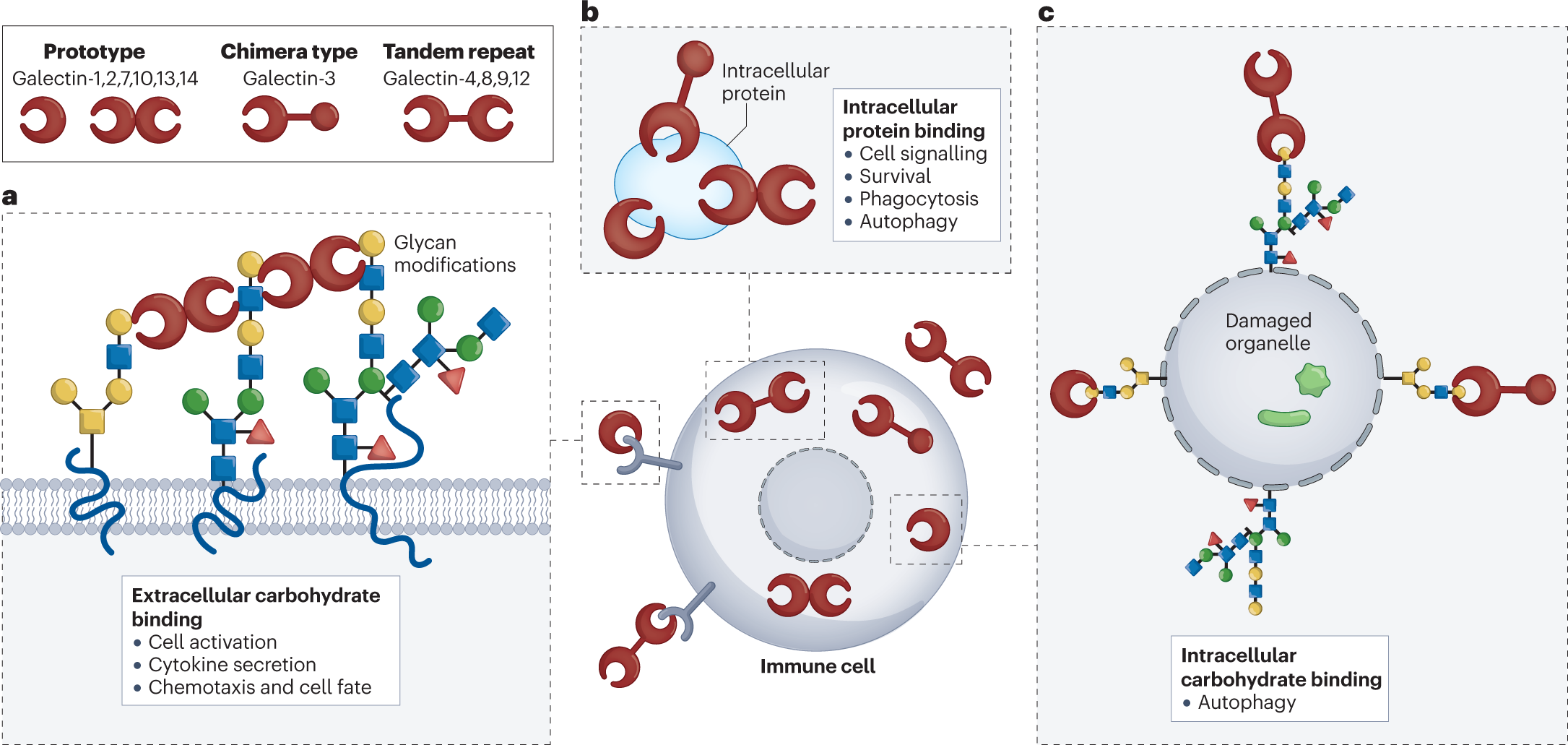
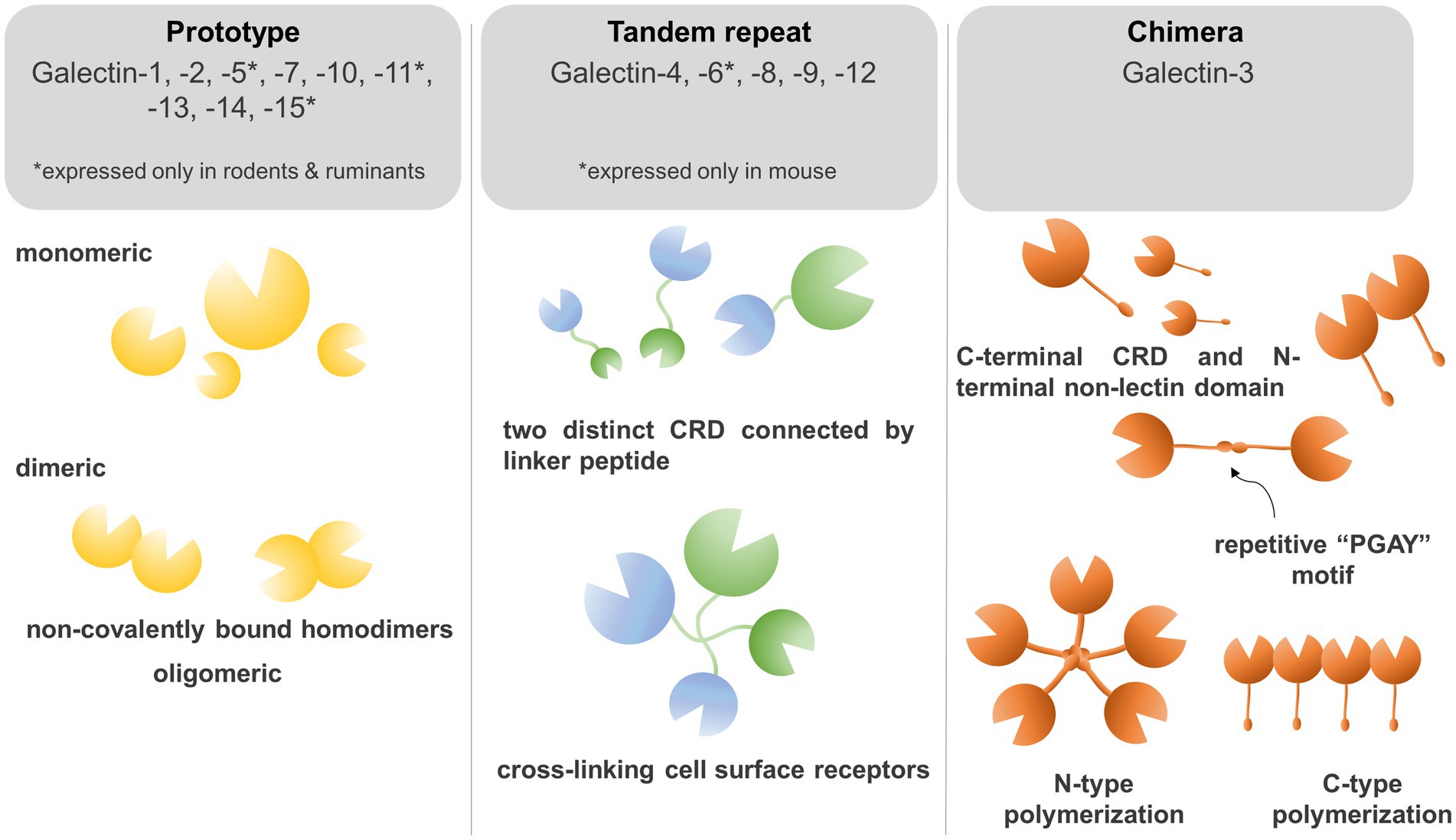
Carbohydrate Recognition: Galectins recognize carbohydrate moieties on intracellular ligands, cell signaling receptors, and extracellular matrices, playing crucial roles in immune responses 8.
-
Galectin-1 in Innate Immune Response: Galectin-1 promotes the resolution of acute inflammation and has a pivotal role in the innate immune response 9.
These findings underscore the multifaceted roles of galectins and their ligands in modulating immune responses and inflammation. The images provided in the search results further illustrate the complex interactions and roles of galectins in inflammation and immune responses. For instance, one image from a research article depicts the multifunctional roles of galectins in mucosal intestinal inflammation 10.
Follow Up
Related
In what ways do Galectins and their ligands influence the inflammatory response?
What was the focus of Roberto Paganelli's research on electromagnetic fields?
What role does Roberto Paganelli play in the journal Pathogens?
What role does the intracrine mechanism play in regulating intracellular events?