Reference

Reference



Moonshot's Answer
The immune responses in normal and milk allergic subjects differ significantly, particularly in terms of antibody production and types, cellular responses, and the overall allergic reaction. Here's a summary based on the search results:
-
Antibody Production: Non-atopic individuals typically form IgA and IgG complexes, while milk-allergic subjects show a rise in IgA, IgG, IgE, and C1q-binding complexes. This suggests that milk-allergic individuals have a broader and more complex antibody response, particularly involving IgE, which is a key player in allergic reactions source.
-
Cellular Responses: Both infants with and without allergy to cow's milk have a CMP-specific T helper cell response. However, the nature and intensity of this response may differ, contributing to the development or prevention of allergy symptoms source.
-
Allergic Reactions: Milk-allergic subjects are more likely to exhibit hypersensitivity reactions to cow's milk proteins, which can be IgE-mediated or involve other immune mechanisms. This contrasts with normal subjects who do not exhibit such reactions source.
-
Regulation of Immune Response: Maternal milk can regulate the immune response to -lactoglobulin in allergy, suggesting differences in how immune responses are modulated between allergic and non-allergic subjects source.
-
Immunologic Properties: The immunologic and allergic properties of cow's milk proteins can lead to abnormal immunologic responses in milk-allergic individuals, highlighting the role of specific milk proteins in triggering allergic reactions source.
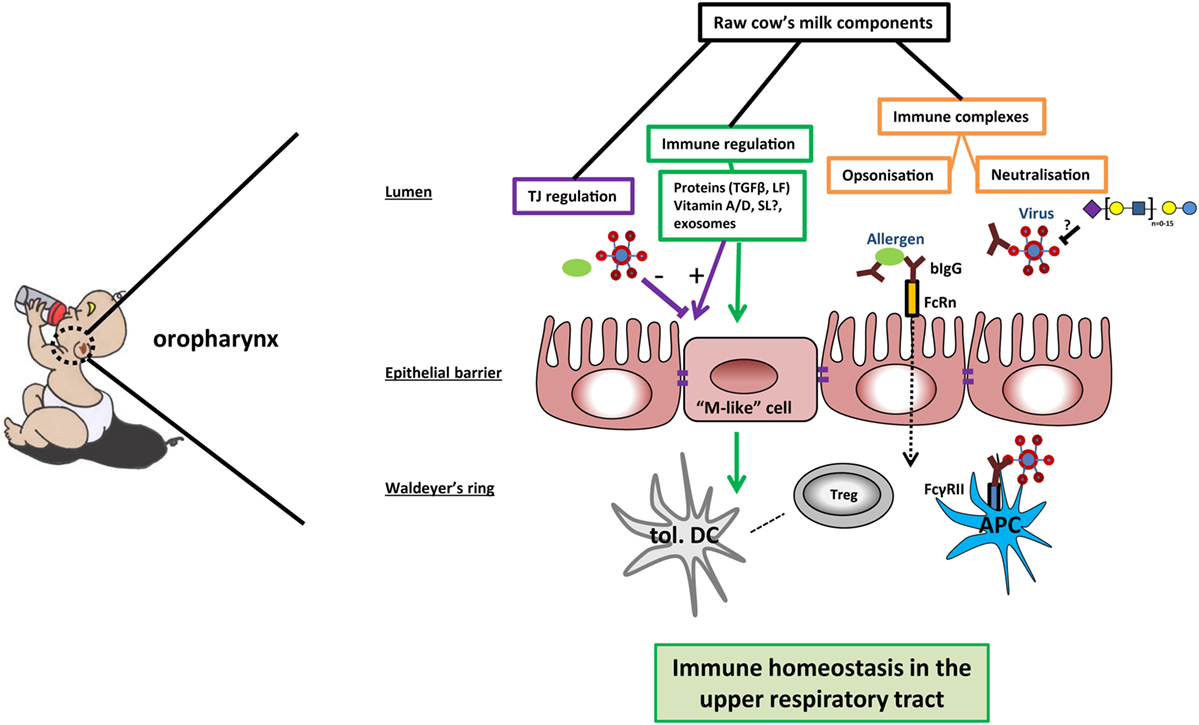
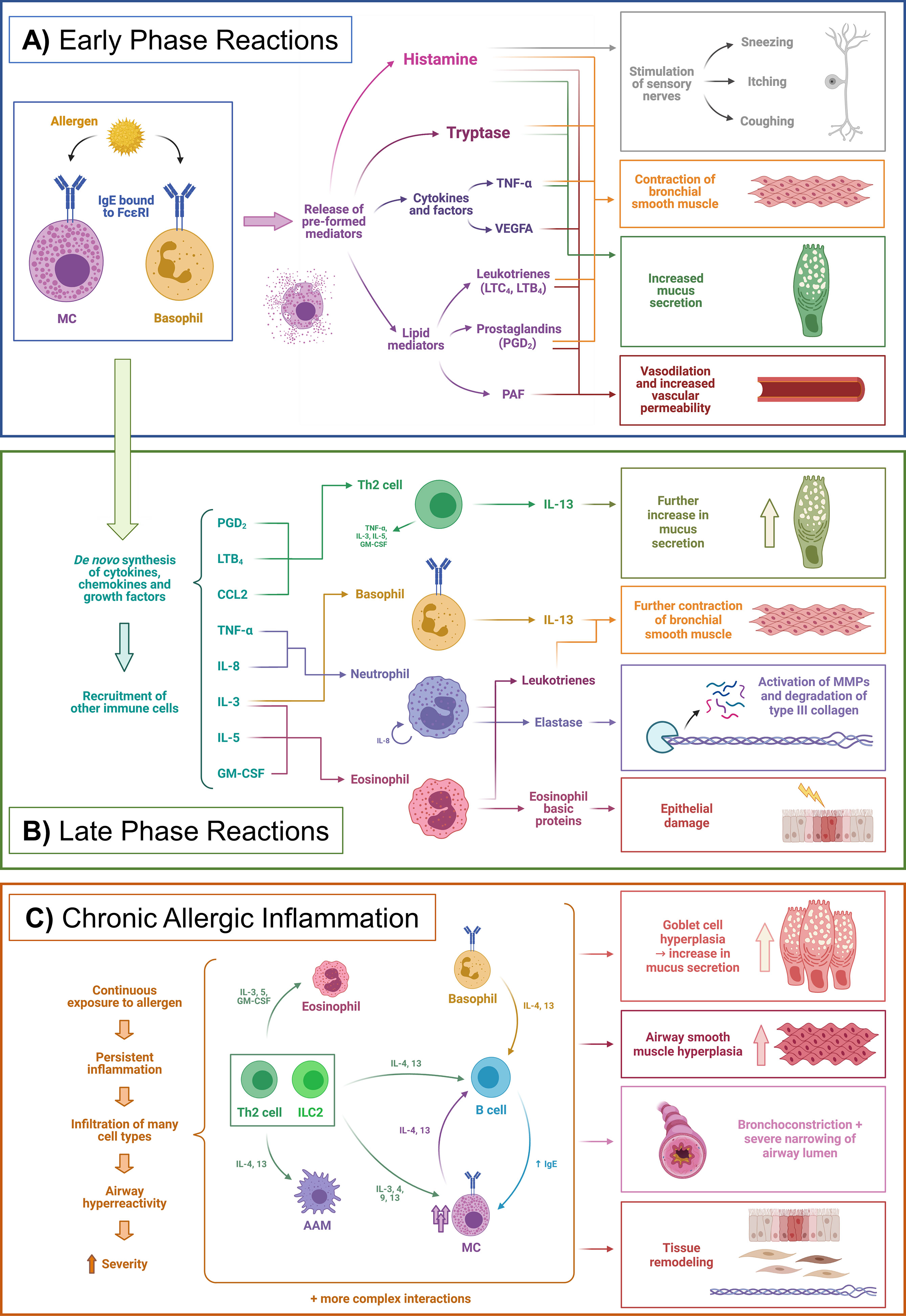
To visualize these differences, you can refer to images that depict the immune response in allergic versus tolerant states for cow's milk proteins, showing the complexity of the immune response in allergic individuals image source. These findings underscore the importance of understanding the immune system's role in food allergies and the development of appropriate therapeutic strategies.
Follow Up
Related
What effects do electromagnetic fields have on the immune system in women?
How does the allergenicity of goat's milk affect children with cow's milk allergy?
How does goat's milk allergenicity compare to cow's milk in children?
What areas of research has Roberto Paganelli focused on in his career?