Reference



OpenAI's Answer
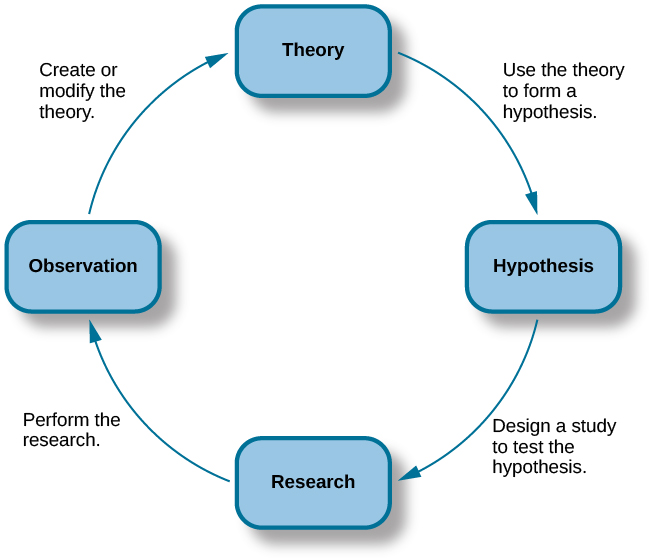
Experimental confirmation is crucial for theoretical thought experiments for several reasons:
-
Validation of Predictions: Thought experiments often lead to hypotheses or predictions. Experimental confirmation validates these predictions, lending credibility to the theoretical framework.
-
Detection of Inconsistencies: As noted in Probing theoretical statements with thought experiments, thought experiments can reveal inconsistencies within existing theories. Experiments help identify and resolve these discrepancies.
-
Empirical Basis: The process of scientific inquiry heavily relies on empirical data. The practical application of theories through experiments ensures that they are not only logically sound but also empirically grounded. This is aligned with the hypothetico-deductive approach, which emphasizes testing and refutation as key to scientific progress.
-
Refinement of Theories: Experimental results can lead to the refinement and development of theories. The feedback loop between theory and experiment is essential in advancing scientific knowledge.
-
Philosophical Significance: The ongoing debate about thought experiments highlights the necessity for a balance between theoretical constructs and empirical verification. The philosophy of experimentation emphasizes the importance of intervention and production in validating thought experiments (The philosophy of scientific experimentation).
In summary, experimental confirmation is integral to ensuring that theoretical thought experiments hold practical and scientific value.