Reference


OpenAI's Answer
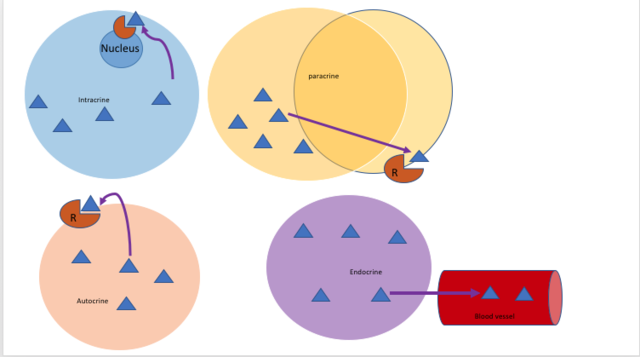
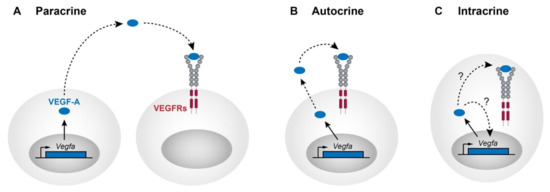
The intracrine mechanism plays a crucial role in regulating intracellular events by allowing signals to act within the same cell where they are synthesized. This type of signaling involves the production of a chemical signal by the cell, which then acts on receptors located within the cytoplasm or nucleus of the same cell, thereby regulating various intracellular processes.
-
Cell Growth and Survival: Intracrine signaling pathways, such as those involving VEGF-A, are significant in regulating cell growth and survival. By acting internally, these signals can help cells manage growth processes and respond to stress or survival cues effectively (source).
-
Fine-Tuning Hormonal Responses: Intracrine mechanisms allow for the fine-tuning of hormone levels, including sex hormones like estrogen, within tissues and organs. This helps in meeting the physiological needs of the body by controlling the exposure of tissues to these hormones (source).
-
Control of Intracellular Events: Intracrine signaling is involved in regulating essential intracellular events, such as DNA synthesis and gene expression. This regulation is critical for maintaining cellular function and integrity.
-
Cancer and Stem Cell Regulation: In the context of diseases such as cancer, intracrine signals may help regulate the behavior of cancer stem cells, influencing tumorigenesis and tumor progression (source).
Here's an illustration depicting different mechanisms of cell signaling, including intracrine signaling:

Overall, the intracrine mechanism ensures that cells have robust control over their internal environments, thus influencing various physiological and pathological processes.
Follow Up
Related
What historical event does Neda Ulaby reference in the NPR piece from May 2008?
What event leads Crusader to take the reality-altering ring for himself?
What special Doctor Who events have been held on stage or live?
What are the major cycle routes and cycling events in Wales?
How did the historical events, such as uprisings and wars, impact these synagogues?