Reference


OpenAI's Answer
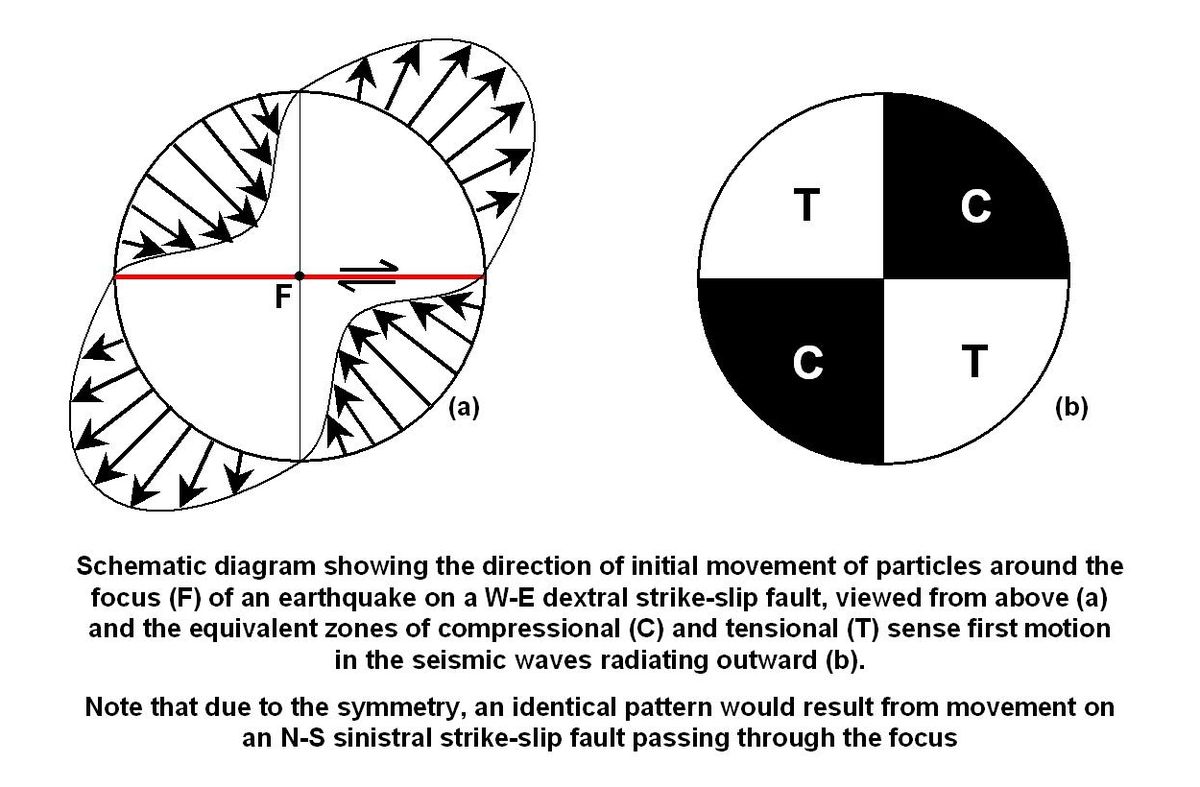
The focal mechanism of an earthquake describes the deformation in the source region that generates seismic waves. It provides information about the fault orientation and the slip direction during an earthquake. This is often visualized using a "beach ball" diagram, which is a graphical representation of the faulting motions. These diagrams help seismologists understand the type of faulting that occurred, such as normal, reverse, or strike-slip faulting.
Key Points about Earthquake Focal Mechanisms:
- Fault Orientation and Slip Direction: The focal mechanism indicates the orientation of the fault and the direction in which the fault slipped during the earthquake.
- Beach Ball Diagrams: These are used to visually represent the focal mechanism. The pattern of shading and lines in the diagram helps identify the type of faulting.
- Types of Faulting: The focal mechanism can indicate different types of faulting, such as normal, reverse, or strike-slip, based on the movement along the fault.
For more detailed information, you can refer to the following resources:
- Wikipedia on Focal Mechanism
- USGS Explanation on Earthquake Focal Mechanisms
- IRIS Animation on Focal Mechanisms
Here is an example of a beach ball diagram used to represent focal mechanisms:

These diagrams are crucial for understanding the seismic activity and the stress distribution in the Earth's crust.
Follow Up
Reference




Moonshot's Answer
The focal mechanism of an earthquake describes the deformation in the source region that generates the seismic waves. It provides information about the fault orientation and the slip direction of the earthquake. Seismologists often use a graphical representation called a beach ball diagram to illustrate the focal mechanism. These diagrams show the fault plane solutions and the direction of slip on the fault, which can be used to understand the type of deformation that occurred during the earthquake.
Here is an example of a focal mechanism diagram, also known as a beach ball plot, which visually represents the earthquake's focal mechanism:  . This image is a typical representation used by seismologists to depict the complex data of an earthquake's focal mechanism in a more understandable format.
. This image is a typical representation used by seismologists to depict the complex data of an earthquake's focal mechanism in a more understandable format.
For more detailed information, you can refer to resources such as the Wikipedia page on Focal Mechanism or the Incorporated Research Institutions for Seismology (IRIS), which provides animations and explanations on the topic.