Reference



OpenAI's Answer
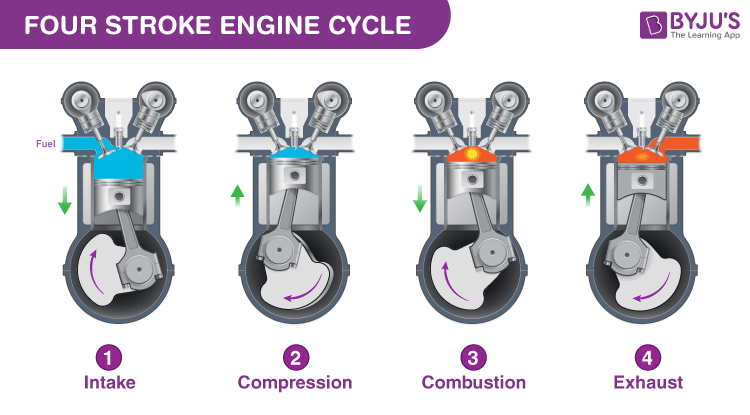
A four-stroke petrol engine is a type of internal combustion engine that completes four separate strokes—intake, compression, power, and exhaust—during two separate revolutions of the engine's crankshaft. These engines are known for their efficiency, lower emissions, and higher power output compared to two-stroke engines.
Here's a brief explanation of each stroke in the cycle:
-
Intake Stroke: The intake valve opens, allowing a mixture of petrol and air to fill the cylinder as the piston moves down.
-
Compression Stroke: With the intake valve closed, the piston moves back up, compressing the air-fuel mixture. This increases the mixture's temperature and pressure, enhancing combustion efficiency.
-
Power Stroke: A spark from the spark plug ignites the compressed air-fuel mixture, causing the mixture to burn rapidly and expand. The expanding gases push the piston down, creating the power that turns the crankshaft.
-
Exhaust Stroke: The exhaust valve opens, and as the piston moves back up, it expels the burnt gases out of the cylinder, preparing the engine for the next cycle.

This type of engine was first successfully demonstrated by Nicolaus Otto in 1876, and it follows what is known as the Otto cycle. Due to its efficiency and reliability, the four-stroke engine has become the standard for most petrol-powered vehicles today.
For more detailed information, you can refer to the sources below:
- Wikipedia on Four-stroke engine
- Detailed explanation from BYJU'S on Four Stroke Engine
- Overview from Lubrizol360 on Four-stroke Gasoline Process
Follow Up
Reference




Moonshot's Answer
A four-stroke petrol engine, also known as a four-cycle engine, is an internal combustion engine where the piston completes four separate strokes while turning the crankshaft to produce power. These four strokes are intake, compression, power, and exhaust. Here's a brief overview of each stroke:
- Intake Stroke: The piston moves down, creating a vacuum that draws an air-fuel mixture into the cylinder through an open intake valve.
- Compression Stroke: The piston moves up, compressing the air-fuel mixture. This compression increases the temperature and pressure of the mixture.
- Power Stroke: The compressed air-fuel mixture is ignited by a spark plug, causing an explosion that forces the piston down, turning the crankshaft and producing power.
- Exhaust Stroke: The piston moves up again, pushing the exhaust gases out of the cylinder through an open exhaust valve.
This cycle repeats, and for every two revolutions of the crankshaft, the engine produces power once. The four-stroke engine was first demonstrated by Nicolaus Otto in 1876 and follows the Otto cycle, which is why it's also called the 'Otto cycle engine'. It's widely used in automobiles and other applications due to its efficiency and reliability.
Here's an image illustrating the four strokes of a petrol engine:
 Image Source: Byju's
Image Source: Byju's