Reference


OpenAI's Answer
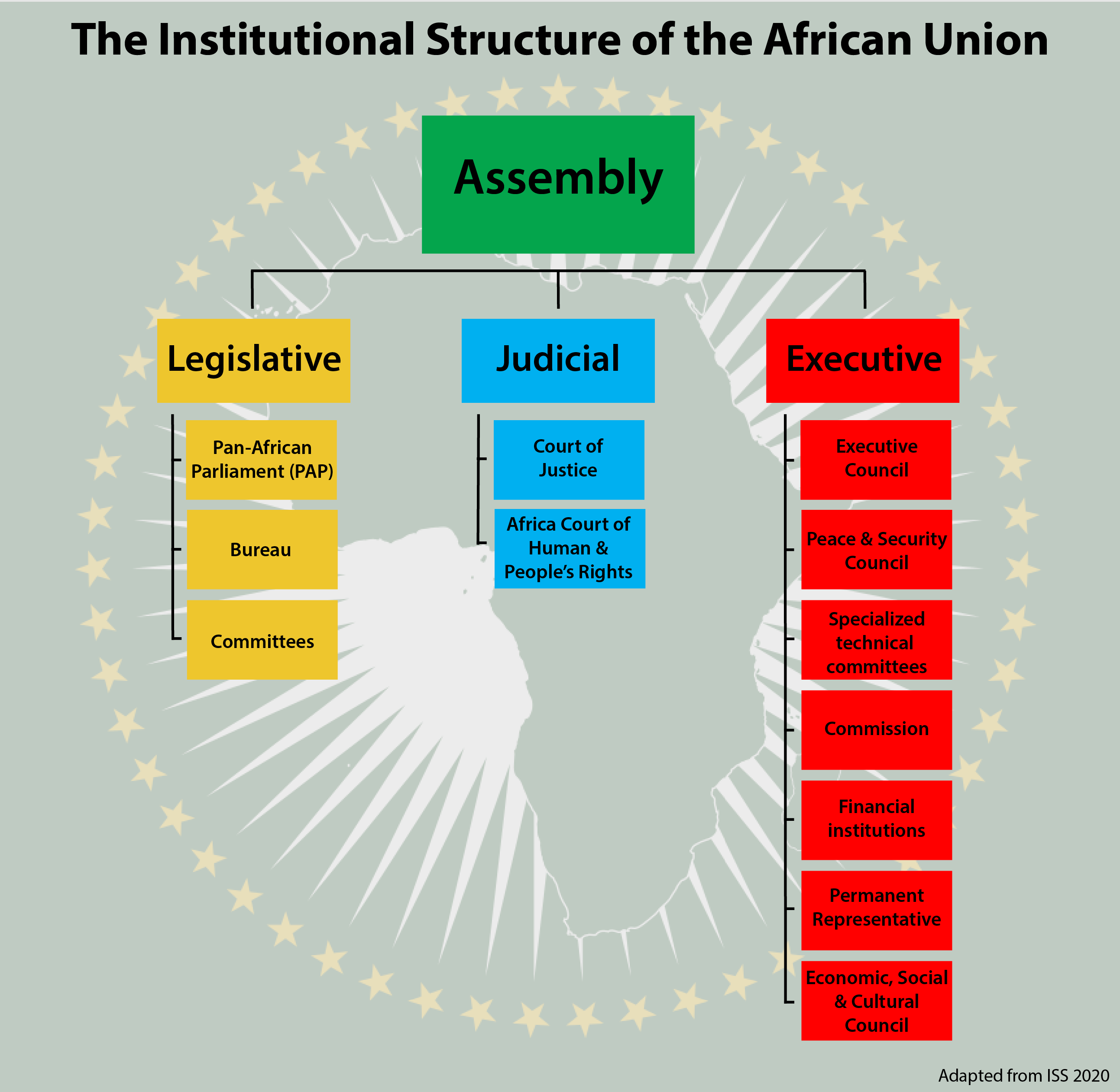
The African Union (AU) is composed of several primary institutions and bodies, each playing a distinct role in its governance and administration. Here are some key components:
-
Assembly of the African Union: The highest decision-making organ, made up of all heads of state or government of the AU member states. It oversees the implementation of AU policies and decisions.
-
Executive Council: Composed of foreign ministers or designated representatives from each member state, it coordinates and makes decisions on common foreign policies.
-
Permanent Representatives Committee (PRC): Consists of permanent representatives of member states, who assist the Executive Council.
-
Commission of the African Union: The AU's secretariat, responsible for executing AU programs and decisions. It is headed by the Chairperson of the Commission.
-
Pan-African Parliament: Acts as a legislative body to provide oversight and consultative input within the AU.
-
African Court on Human and Peoples' Rights: Ensures protection of human and collective rights.
-
Peace and Security Council (PSC): Responsible for peacekeeping and conflict resolution efforts in Africa.
-
Economic, Social, and Cultural Council (ECOSOCC): Serves as a platform for civil society to participate in AU activities.
-
Regional Economic Communities (RECs): Serve as building blocks for economic integration across the continent.
-
Financial Institutions: Includes the African Central Bank, the African Monetary Fund, and the African Investment Bank, although these are still in the development phase.
For detailed information, you can refer to the African Union's official website.
Follow Up
Related
Repositioning for the future: African hand-washing innovation Shesha Geza streamlines its strategi
How does the African Standby Force contribute to the African Union's mission?
Repositioning for the future: African hand-washing innovation Shesha Geza streamlines its strategi
Which South African township was a cultural center for African jazz before its destruction?