Reference


OpenAI's Answer
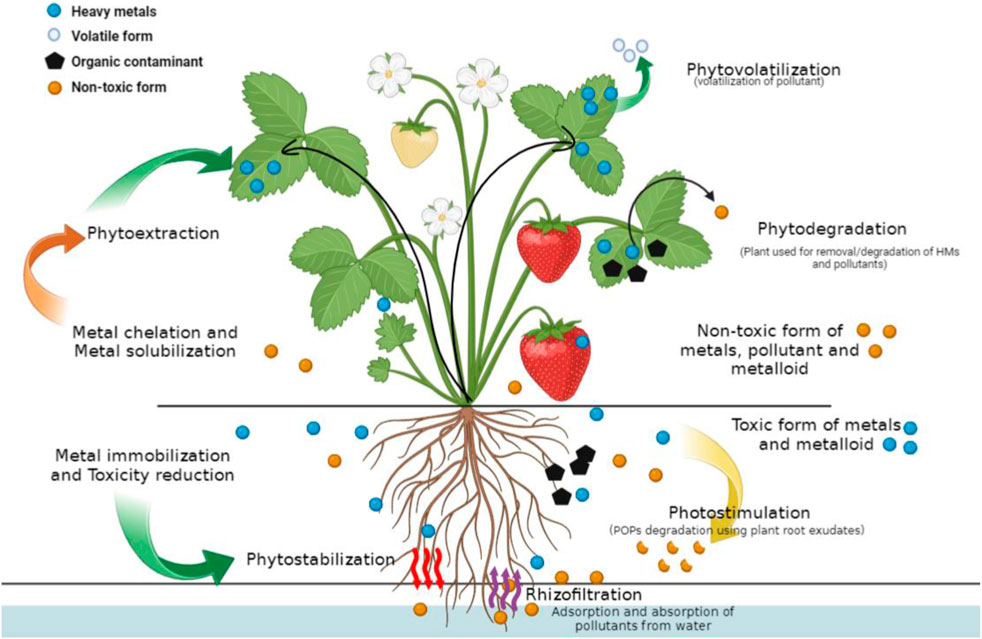
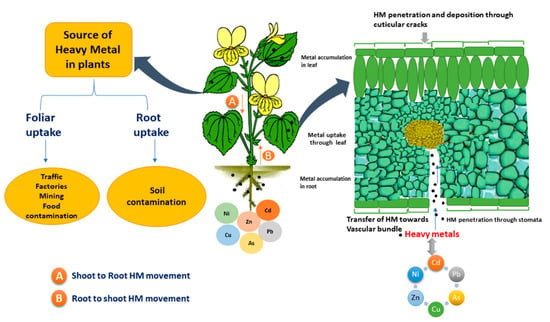
Plant-assisted bioremediation, also known as phytoremediation, is a sustainable and cost-effective method used to clean up heavy metal-contaminated areas. Here are some key applications of this technique:
-
Soil Decontamination: Plants such as Indian mustard, sunflower, and poplar trees are used to extract heavy metals like lead, cadmium, and zinc from contaminated soils. These plants can accumulate metals in their tissues, which are then harvested and disposed of safely.
-
Water Treatment: Aquatic plants like water hyacinth and duckweed are effective in removing heavy metals from water bodies. They absorb metals from the water, thereby reducing contamination levels.
-
Stabilization of Contaminants: Certain plants can stabilize heavy metals in the soil, preventing them from leaching into groundwater. This is particularly useful in areas where soil erosion or water runoff could spread contamination.
-
Rehabilitation of Mining Sites: Phytoremediation is used to rehabilitate areas affected by mining activities. Plants help in restoring the soil structure and fertility, making the land usable again for agriculture or forestry.
-
Urban and Industrial Areas: In urban settings, phytoremediation can be applied to clean up brownfield sites, which are often contaminated with heavy metals due to industrial activities. This not only detoxifies the land but also improves the aesthetic value of the area.
-
Agricultural Land Recovery: In agricultural lands contaminated with heavy metals, phytoremediation helps in reducing metal concentrations, making the soil safe for crop production again.
These applications highlight the versatility and effectiveness of plant-assisted bioremediation in addressing environmental pollution caused by heavy metals. For more detailed studies and examples, you can refer to scientific articles and case studies available online.
Follow Up
Related
explain about the applications of machine learning algorithms
explain about the applications of machine learning algorithms
What supporting documents are required for a B1/B2 visa interview?
larger language model
What resources are available for research on phytoremediation techniques and applications?