Reference



OpenAI's Answer
There are several industrial alternatives to traditional solvent-based paint curing methods, offering various advantages including reduced environmental impact and improved safety. Here are some notable alternatives:
-
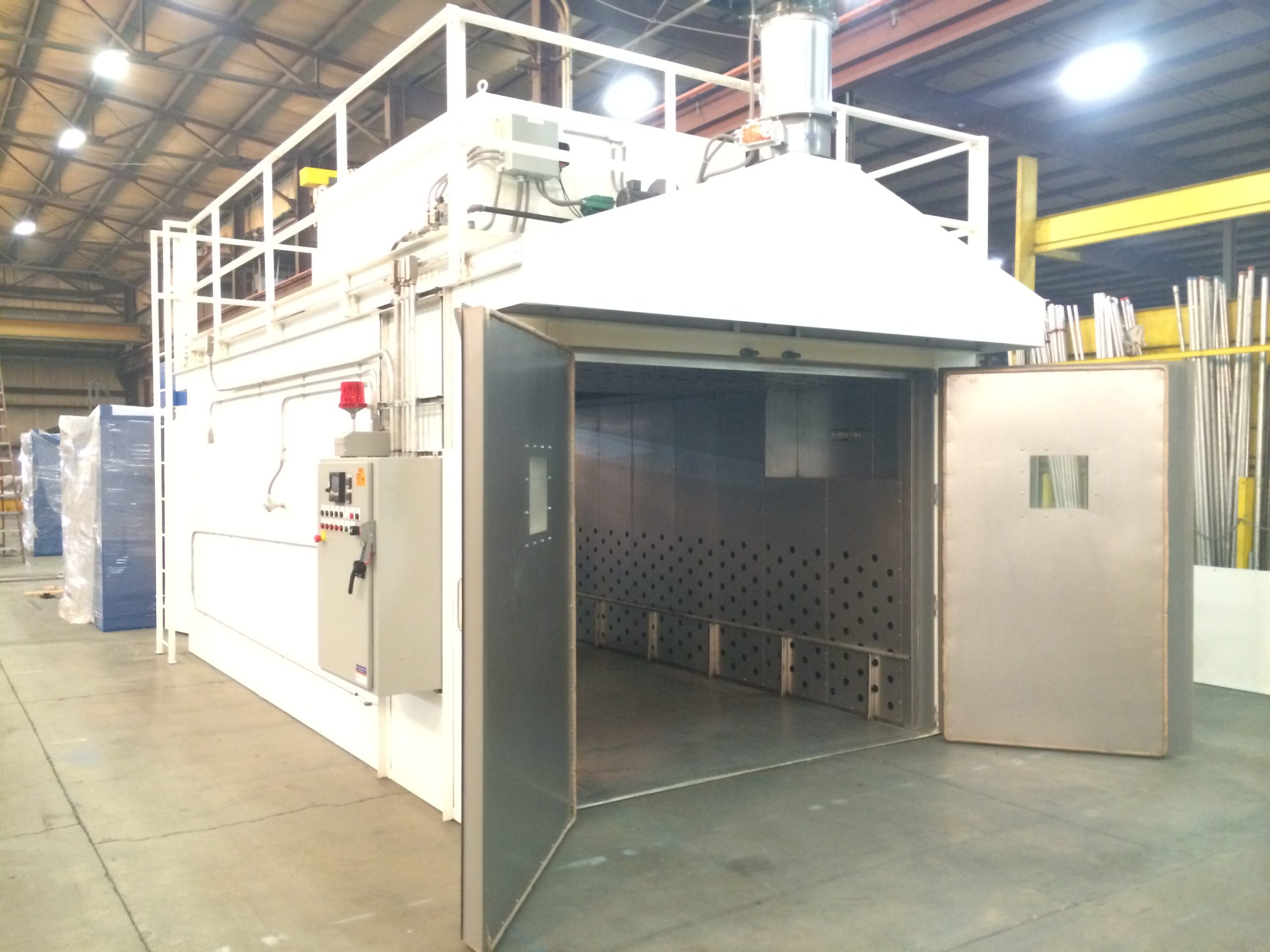
Heat Curing: This involves using ovens to ensure objects coated with solvent-based, water-based, or powder coatings cure effectively at controlled temperatures. This method is quite flexible, allowing for use with different types of coatings, including baked chemistries (Sheboygan Paint Company).
-
Water-based Coatings: Waterborne coatings, such as self-crosslinking acrylic emulsions and polyurethane dispersions, serve as excellent alternatives to solvent-based coatings. They offer good chemical resistance, durability, hardness, and adhesion to surfaces, with the significant benefit of reduced volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions (CoatingsTech Magazine).
-
Ultra-High-Solid Paints: These paints have low VOC emissions and are used in industries that demand high standards of resistance to corrosion and weathering. They are especially popular in the automotive sector due to their sustainability and protective capabilities (Springer Link).
-
Isocyanate-Free Polyurethane Technology: In applications such as automotive refinish, isocyanate-free technologies are being developed to enhance curing times and mechanical properties without the health hazards associated with isocyanates (CoatingsTech Magazine).
These alternatives not only minimize environmental impact but also enhance safety and efficiency in industrial paint applications.
Follow Up
Related
What role does the concept of 'private world' versus 'common world' play in Philip K. Dick's views o
What alternatives exist to plastic-based paints and what are their costs?
How do alternative mRNAs for placenta growth factor originate from a single gene?
Are there alternative spliced transcript variants of the ANXA13 gene?