Reference




Reference
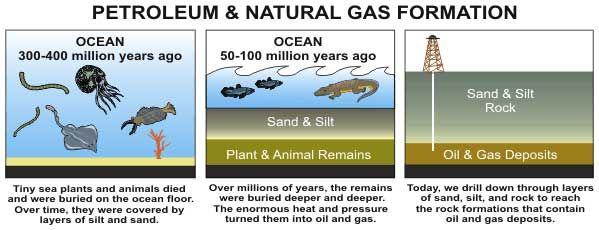



Moonshot's Answer
Biomarkers found in naturally occurring petroleum are organic compounds that serve as molecular fossils from once-living organisms. They are resistant to biodegradation and can be found in crude oil and sedimentary rocks. Key biomarkers include:
- Hopanes: Derived from the bacterium's outer membrane.
- Steranes: Derived from sterols, which are found in plants, animals, and fungi.
- Triterpenoids: Derived from plant waxes.
- Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs): Formed from the condensation of biological materials.
These biomarkers indicate a biological origin because they retain the basic carbon skeleton of their biological precursors. Their presence in petroleum suggests that the hydrocarbons originated from the decay and transformation of ancient organic matter under heat and pressure over millions of years. The specific composition of biomarkers can reveal information about the age of the source rock, the depositional environment, and the type of biological input, supporting the biogenic theory of petroleum formation.


For more detailed information, refer to the following resources:
Follow Up
Related
How do biomarker chemicals suggest the inclusion of biological material in oil?
What major contributions did Aristotle make to the field of biology?
What contributions has Ian A. Graham made to plant molecular biology?
What evidence exists to support the presence of biological molecules from bacteria in oil?