Reference


Reference




OpenAI's Answer
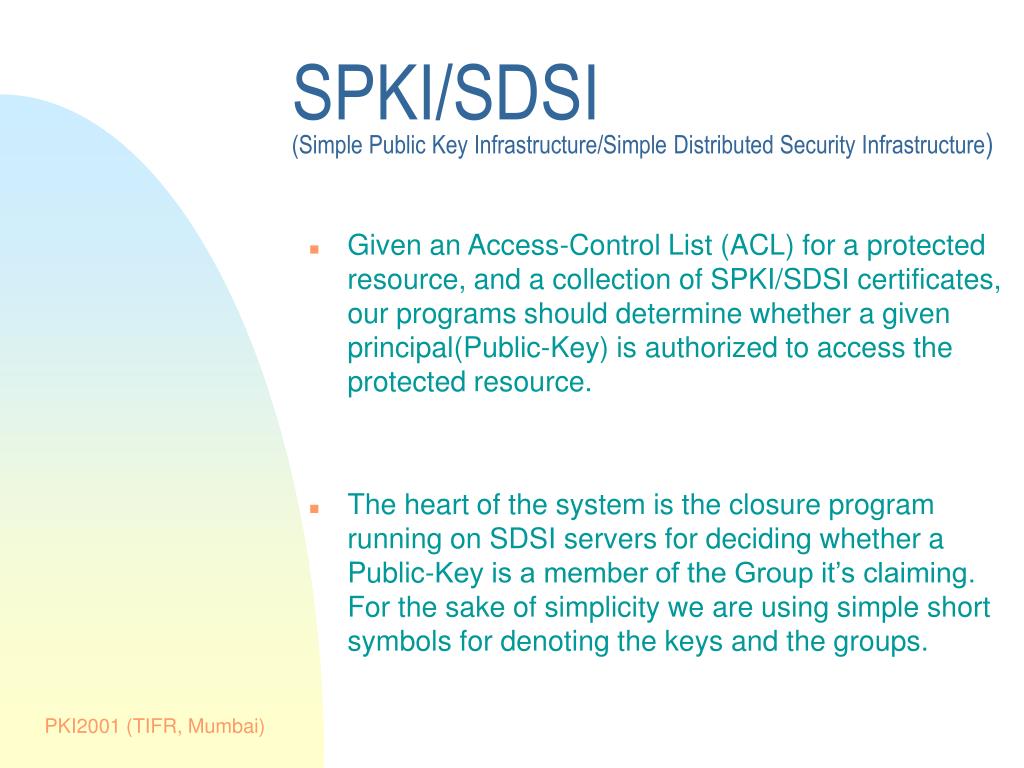
In the realm of public key infrastructure, SPKI (Simple Public Key Infrastructure) and SPKI/SDSI (Simple Distributed Security Infrastructure) use specific encoding formats for managing public keys. Here are some details based on the search results:
-
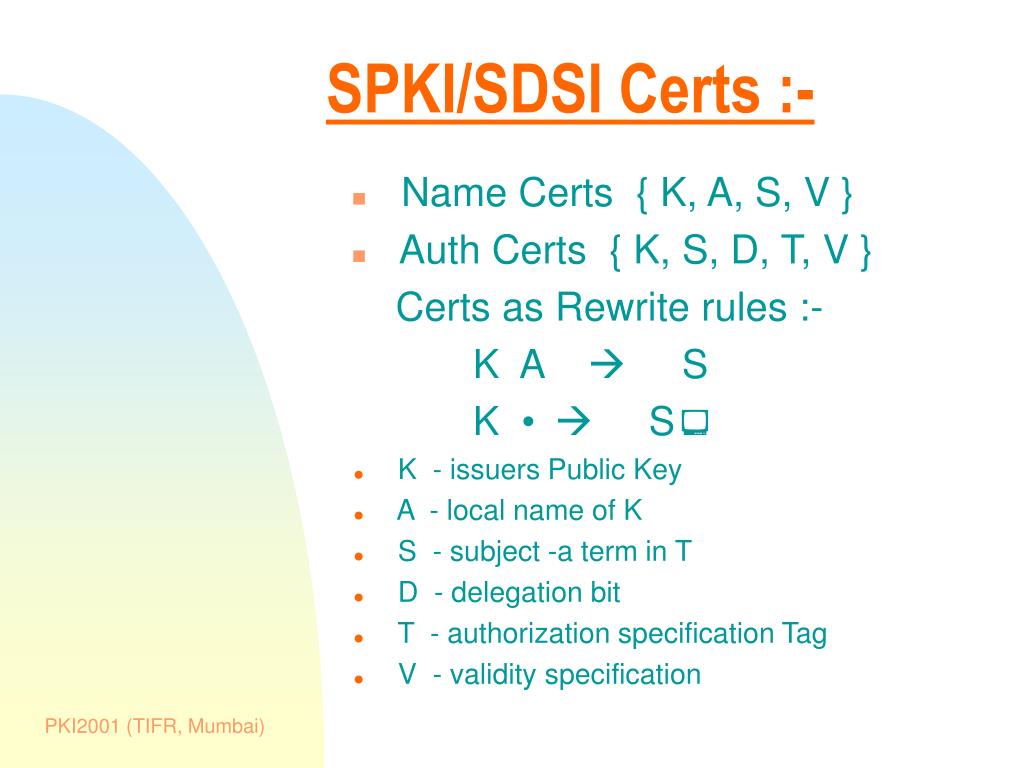
SPKI: In SPKI, the public key certificate format involves encoding for storing, transmitting, and manipulating certificates to support security across various internet applications. The SPKI certificates were originally designed to delineate privileges and bind them to public keys. These certificates can use encoded formats such as S-expressions source.
-
SPKI/SDSI: This combined approach uses S-expressions (a Lisp-like expression format) for encoding. This method is advantageous because it is simple and easily parsed, which aids in the construction, storage, and interpretation of certificates source.
Both SPKI and SPKI/SDSI avoid more complex and cumbersome standards like X.509 in favor of these simpler, more intuitive formats. S-expressions encapsulate the components of the certificate succinctly, helping to maintain simplicity and efficiency.
Here are some visuals depicting the structure and flow in SPKI/SDSI source:

Follow Up
Related
How many human genes encode proteins that belong to the PDGF family?
How does Unicode handle the encoding of Mongolian suffix connectors?
What role does the green fluorescent protein method play in measuring brain activity?
What approach did Wice and Gordon use to isolate cDNAs affecting cell differentiation?